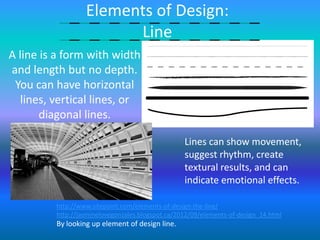
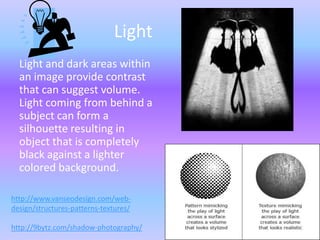
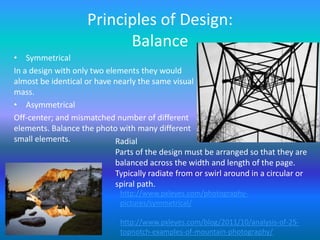
This document discusses the key elements and principles of visual design including:
- Elements such as line, shape, form, color, texture, depth, light, direction, mass, tone, value, space, and time.
- Principles such as balance, emphasis, proportion, repetition, unity, contrast, harmony, proximity, and variety.
It provides examples and definitions for each element and principle, with links to additional online resources. The overall purpose is to define and explain the fundamental components that make up visual composition and design.