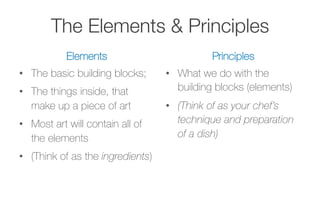
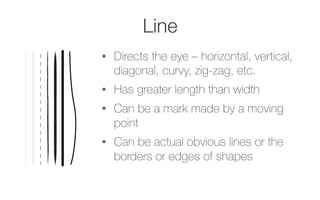
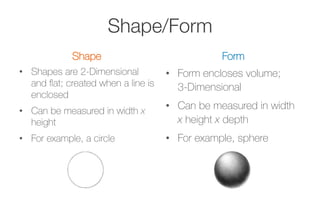
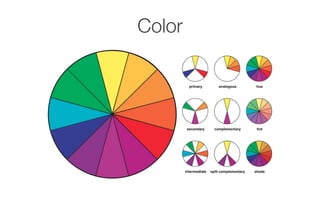
This document provides information about the elements and principles of art and design. It discusses the key elements, which are the basic building blocks that make up a piece of art, such as line, shape, space, value, color and texture. It then covers the principles of design, which are techniques for arranging the elements, like emphasis, balance, unity, contrast, movement and pattern. Students are assigned a project to present examples that demonstrate each element and principle using their own photographs.