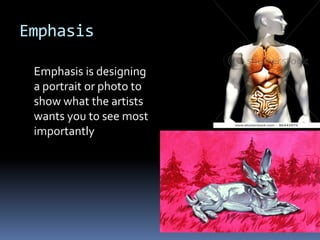
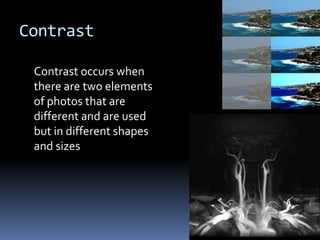
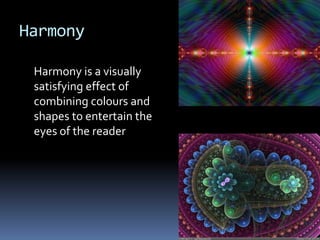
Lines help guide the eye to specific areas of an image. There are three basic types of 2D shapes: geometric, like circles and squares; natural shapes found in nature; and abstract shapes which are modified versions of natural shapes. Form refers to 3D shapes that have volume and can contain solids, liquids or gases. Color, texture, depth, light, direction, mass, tone, value, space, balance, emphasis, proportion, repetition, unity, contrast, harmony, proximity, and variety are all design elements that can be manipulated to achieve different artistic effects in an image.