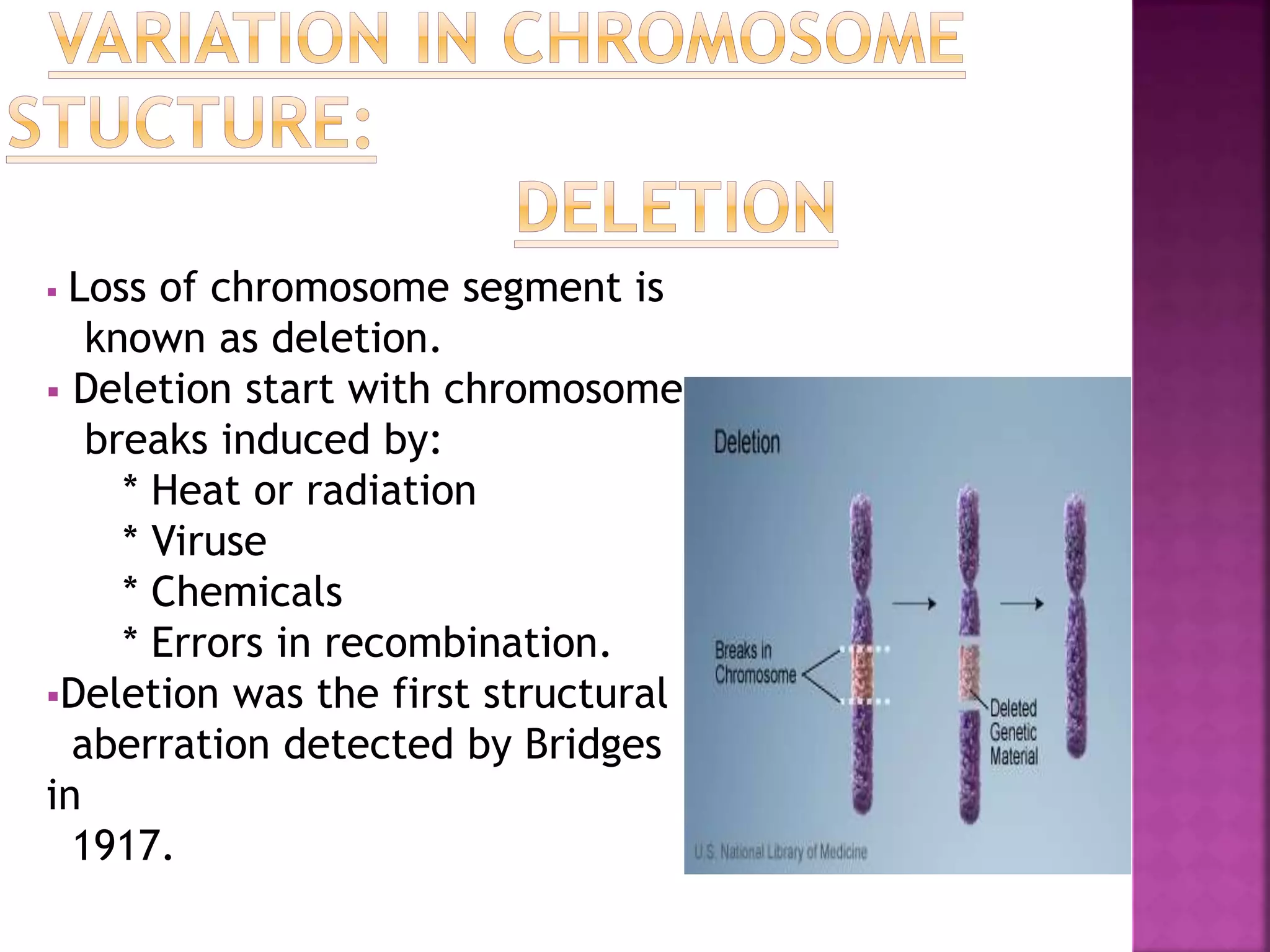
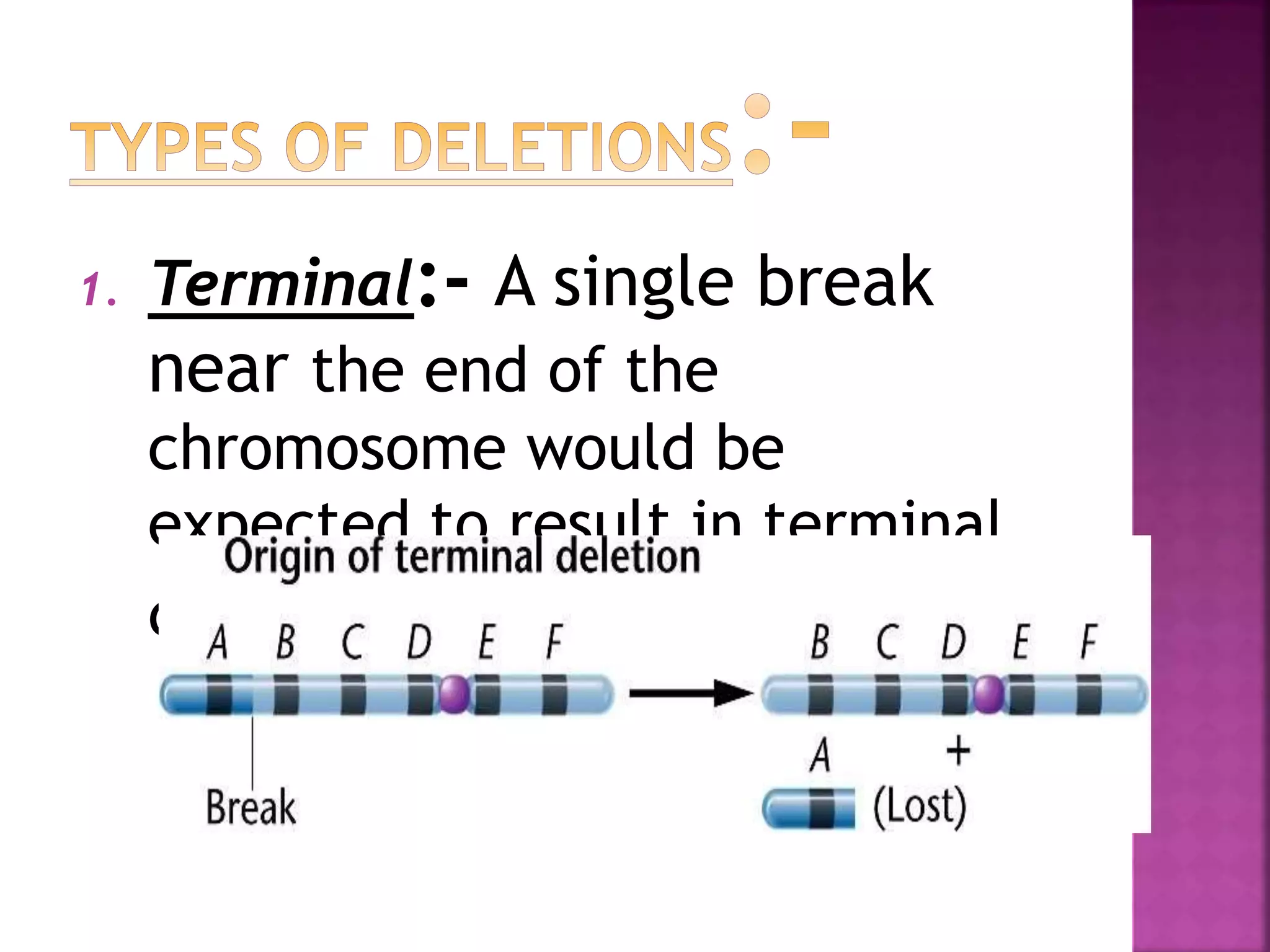
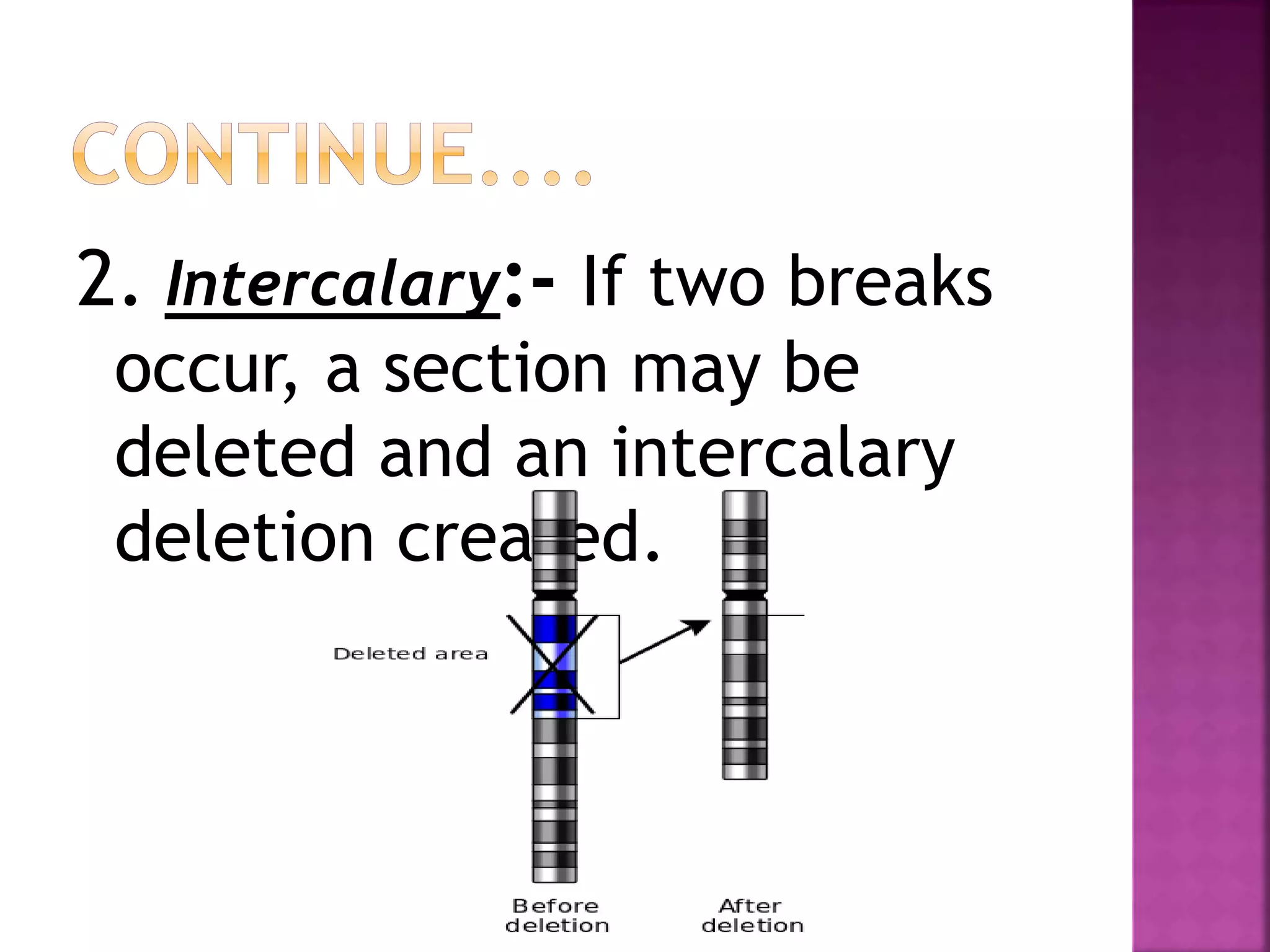
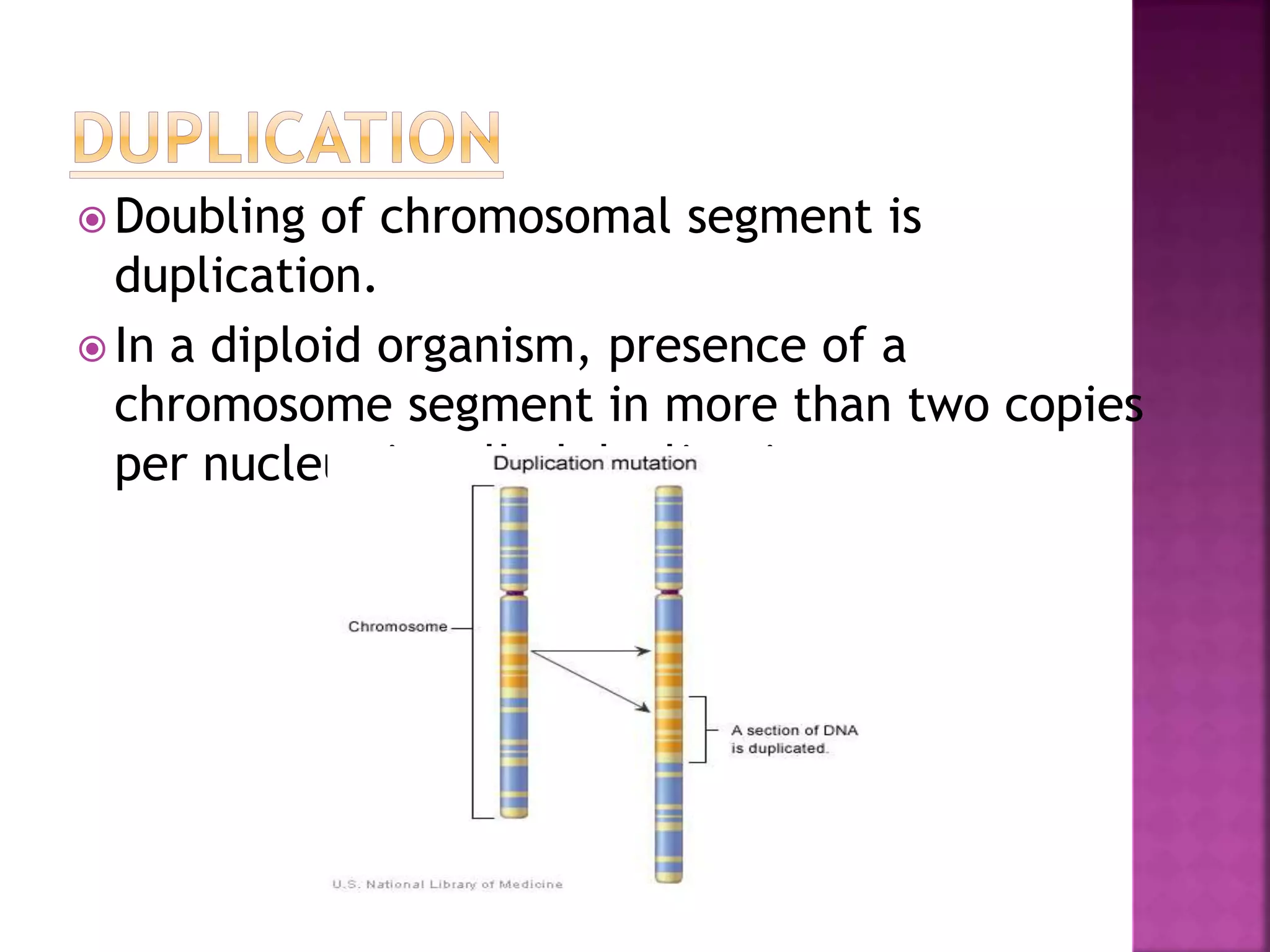
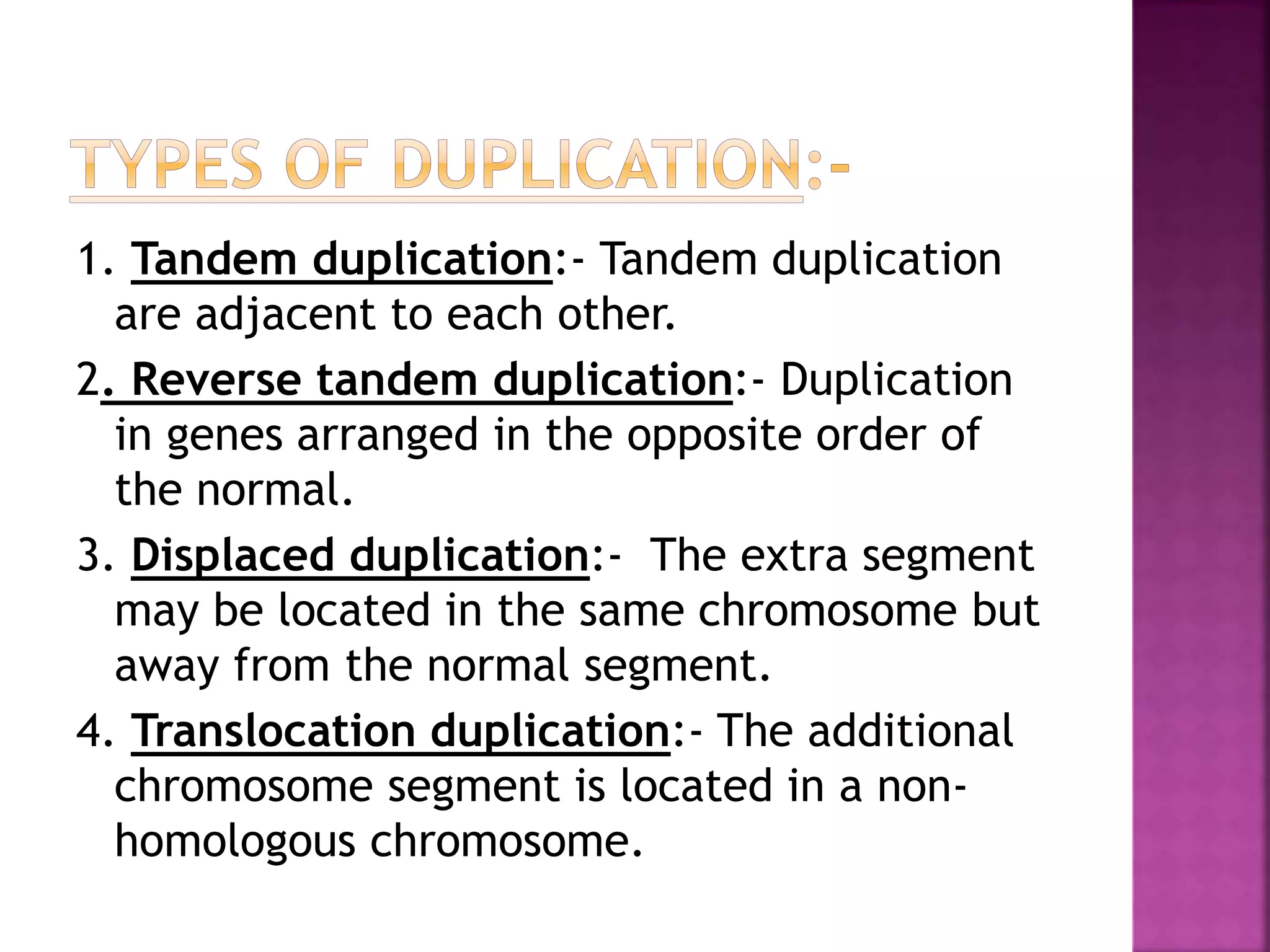
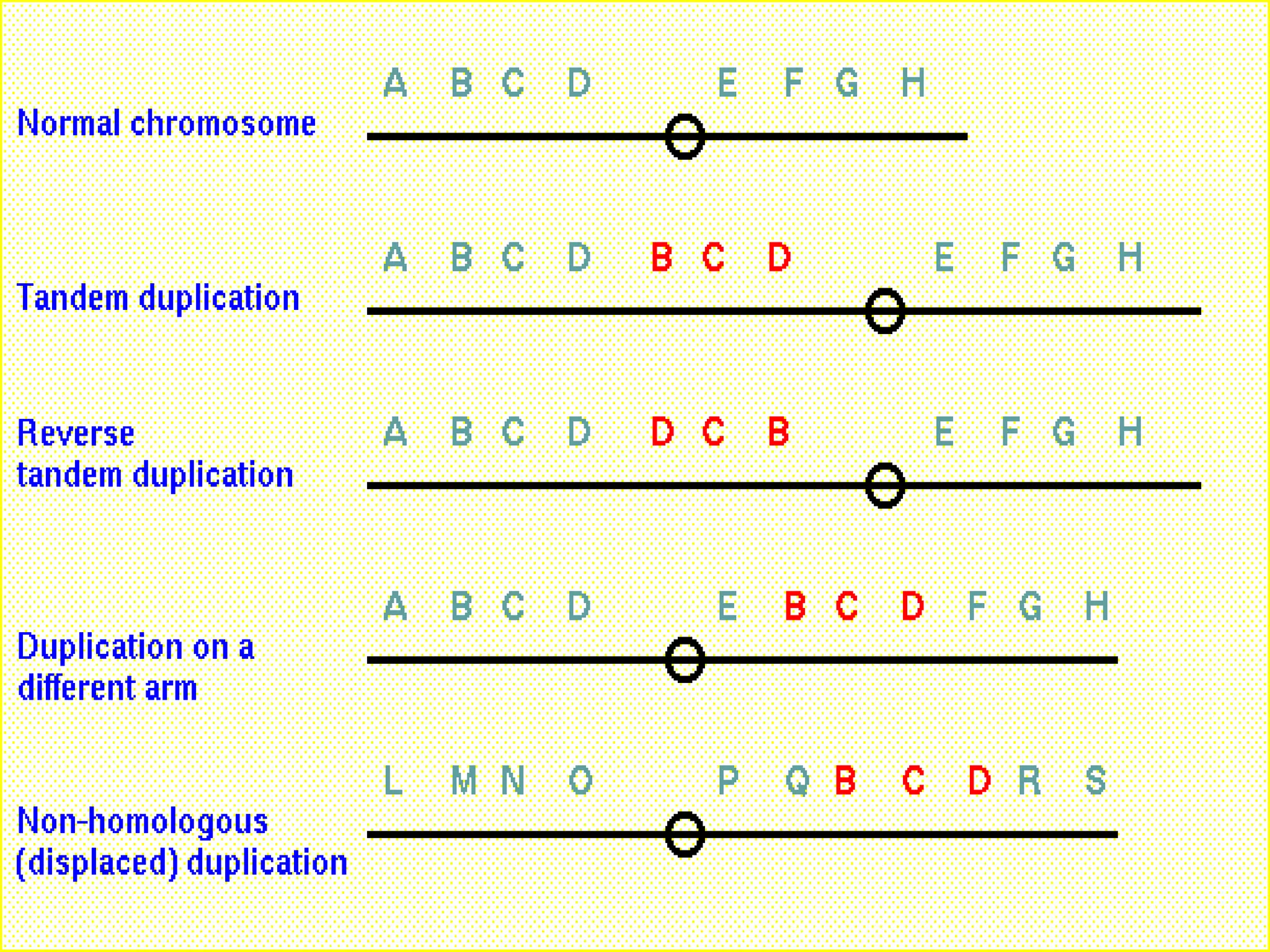
Deletion occurs when there is a loss of a chromosome segment due to factors like heat, radiation, viruses, chemicals, or errors in recombination. It results in the absence of genes in that region. When homozygous, most deletions are lethal as vital genes are missing, while heterozygous deletions leave genes in that region hemizygous with only one copy. Two types of deletions are terminal deletions from breaks near the chromosome end and intercalary deletions from breaks within the chromosome. Examples include cri-du-chat syndrome and myelocytic leukemia.