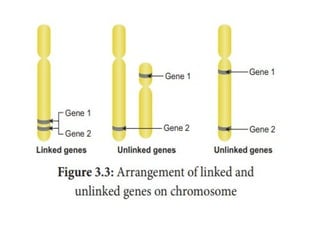
The document discusses genetic linkage, explaining the association of genes on the same chromosome and its impact on inheritance patterns. It details complete and incomplete linkage, emphasizing that linked genes tend to be inherited together unless crossing over occurs. Additionally, it describes two-point and three-point crosses as methods to analyze genetic relationships and determine gene order in organisms.