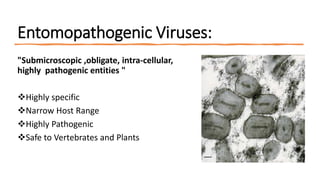
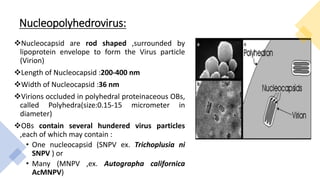
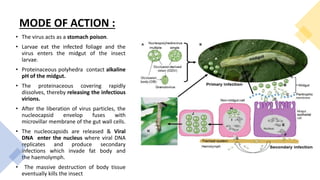
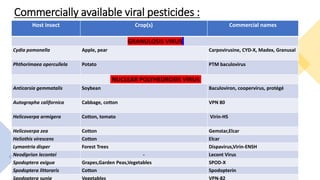
This document presents a presentation on viruses as biocontrol agents. It discusses biological control using microbes like bacteria, viruses, fungi and nematodes. It focuses on entomopathogenic viruses as agents of microbial control. The major families of viruses used for biocontrol are Baculoviridae, Reoviridae, Iridoviridae, Poxviridae, Parvoviridae, Picornaviridae and Rhabdoviridae. Baculoviruses like nucleopolyhedroviruses and granuloviruses are commonly used. Their mode of action involves infecting insect larvae through ingestion. Symptoms include liquefying of body contents and release of viral particles. Some commercially available viral pest