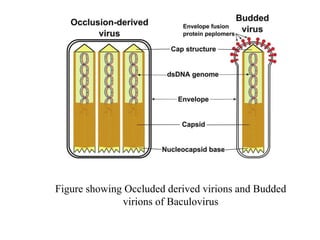
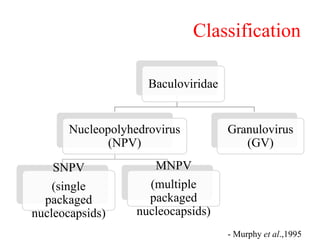
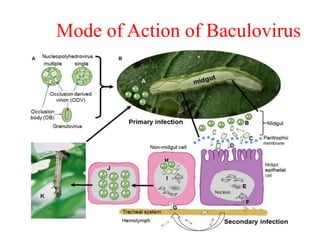
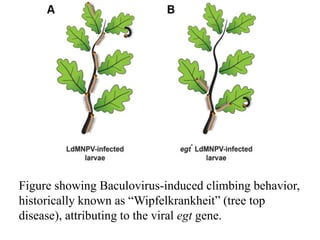
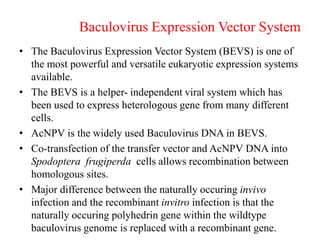
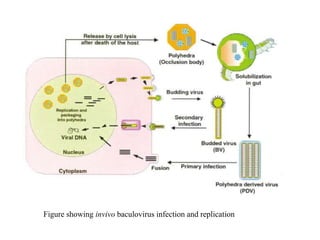
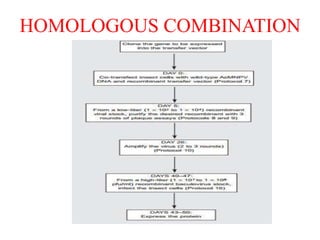
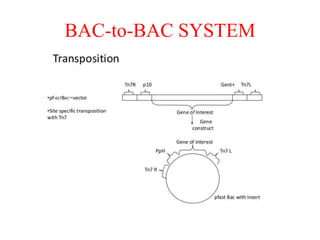
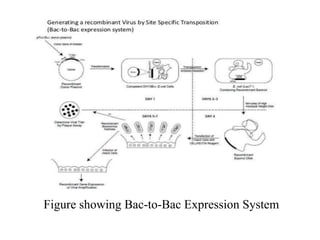
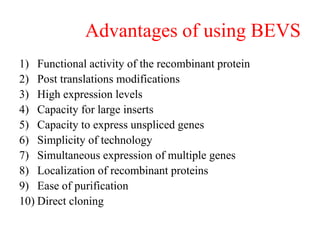
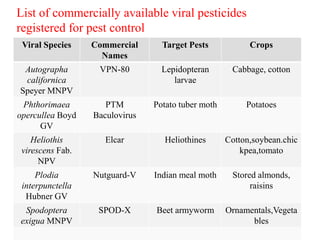
The document discusses baculoviruses, which are lytic viruses primarily pathogenic to insects, detailing their historical influence, structure, and classification. It also covers the mode of action, symptoms of infection, and the baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS) that enables efficient gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Furthermore, it highlights the development of a novel recombinant baculovirus insecticide, Neurobactrus, and the advantages and commercial applications of baculoviruses in pest control and research.