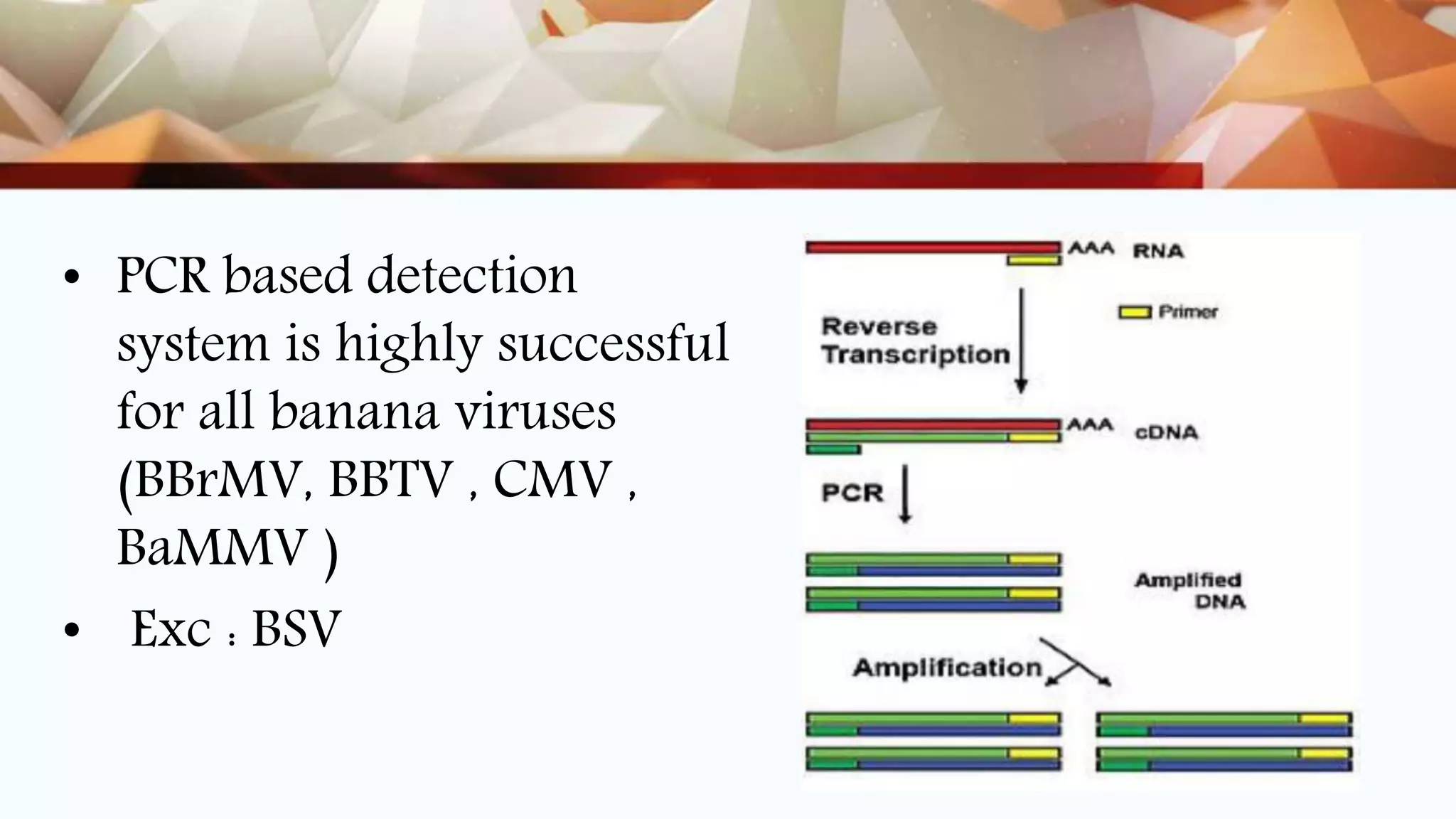
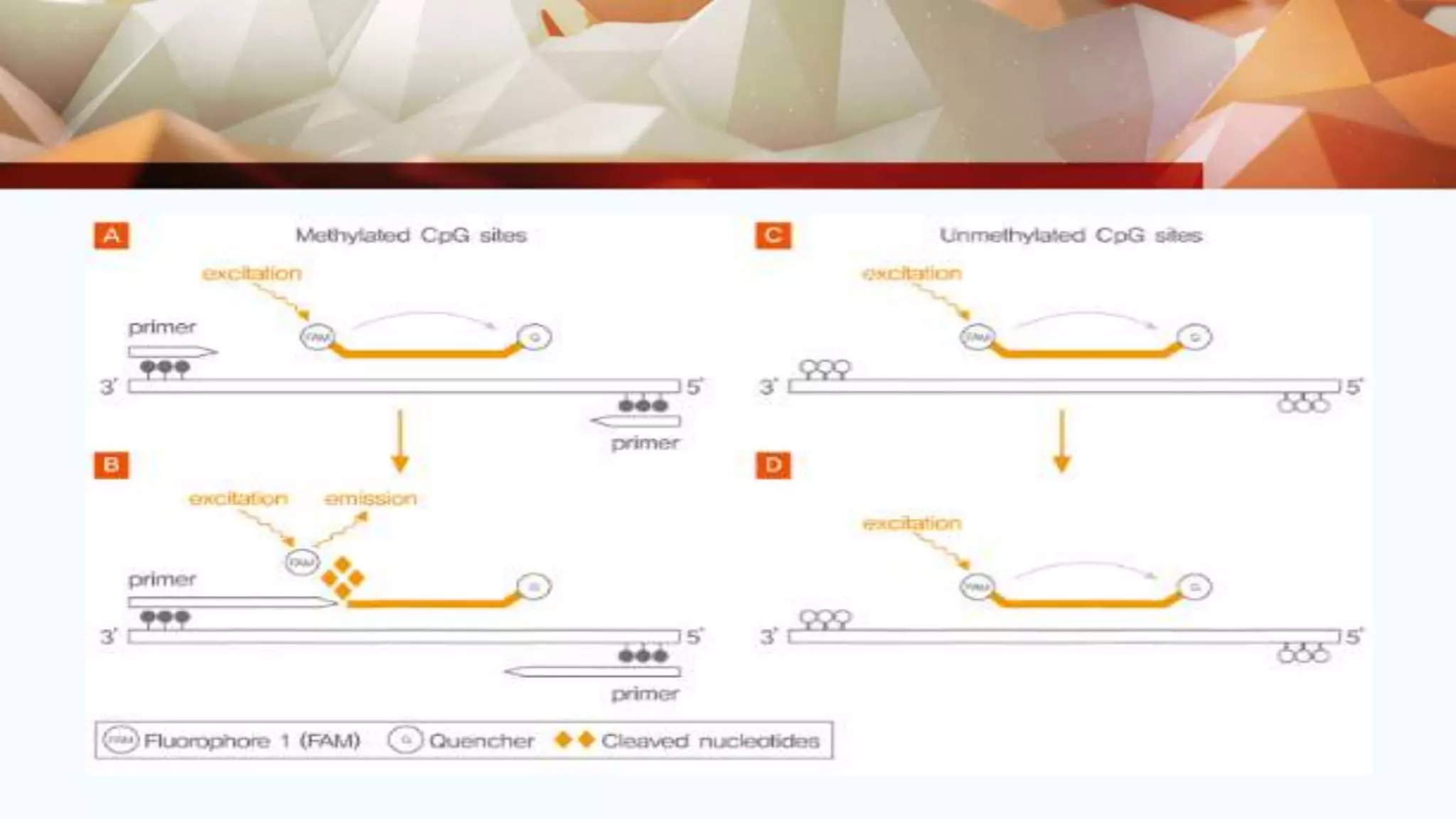
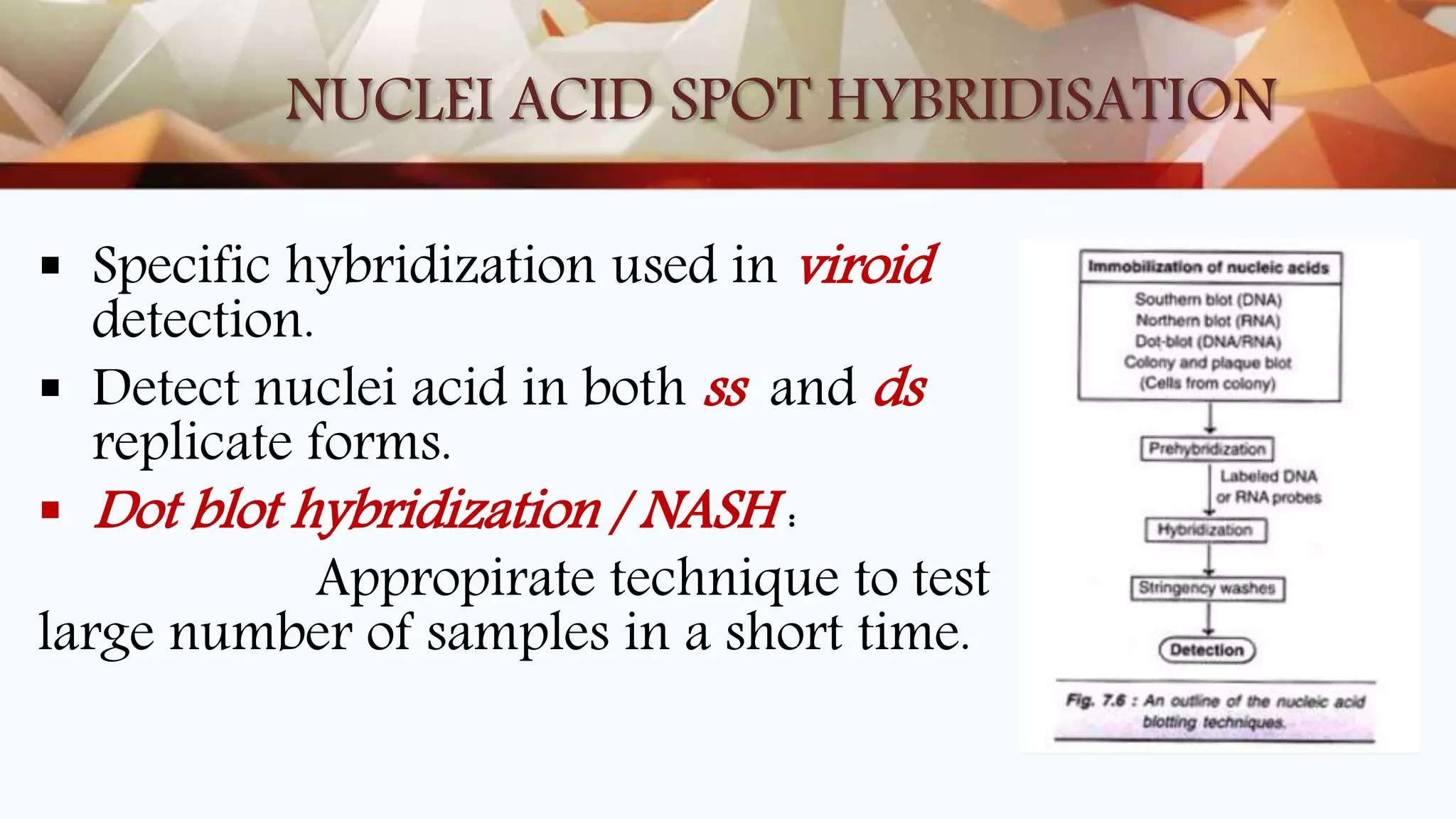
This document discusses various nucleic acid-based methods for virus indexing and detection in plants. It describes techniques like RT-PCR, multiplex PCR, immuno-capture PCR, real-time PCR, nucleic acid spot hybridization, and DNA microarray technology that can be used to detect viral genomes from crude or purified plant samples. Reverse transcriptase PCR is commonly used to detect gene expression and identify infections. Multiplex PCR allows simultaneous detection of multiple viruses. Real-time PCR provides reliable and sensitive quantification of plant viruses. Nucleic acid spot hybridization is suitable for testing large numbers of samples for detection of viruses like BBTV. DNA microarrays can detect a wide range of plant viruses and identify new pathogens through hybridization patterns