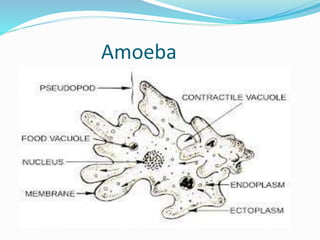
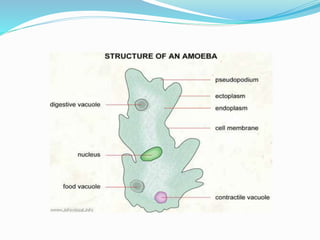
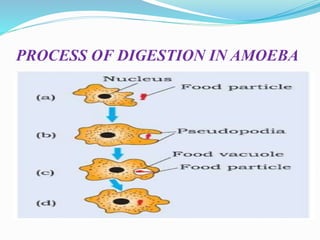
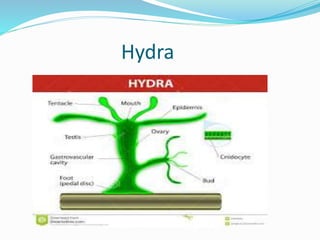
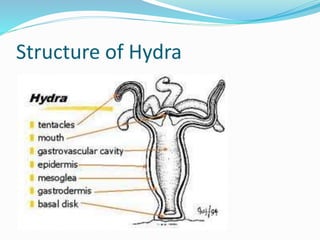
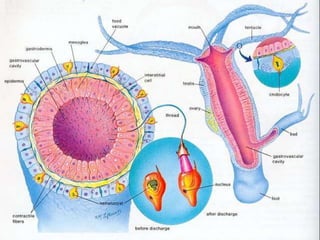
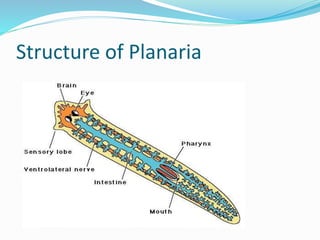
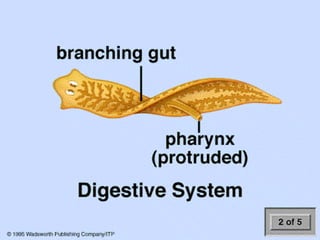
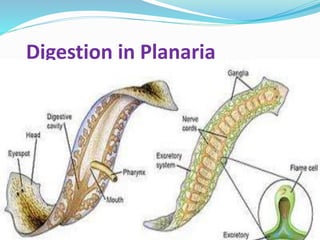
The document discusses nutrition in various lower animals including amoeba, hydra, and planaria. It describes their structures, modes of nutrition, and digestive processes. Amoeba obtains nutrition through holozoic means, ingesting and digesting food intracellularly using food vacuoles. Hydra's mouth opens to a gastrocoel cavity containing glandular cells that secrete enzymes, aiding both extracellular and intracellular digestion. Planaria has a tube-like alimentary canal with a branching intestinal system for digestion, absorption, and distribution of food throughout its body.