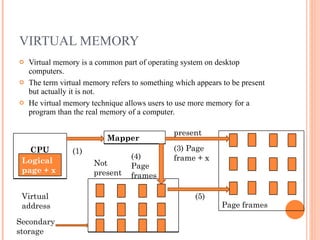
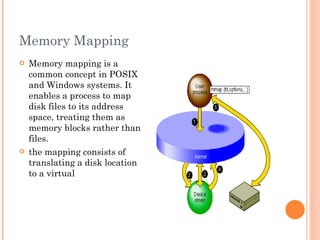
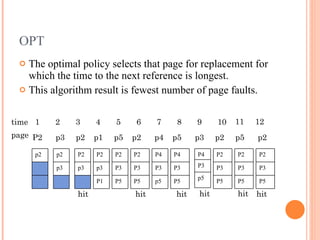
Virtual memory is a technique that allows for more memory to be available to programs than the physical memory installed on the computer. When physical memory is full, infrequently used memory pages are written to secondary storage like a hard disk. This allows processes to access more memory than is physically available. Page replacement algorithms like FIFO, LRU, and OPT are used to determine which memory pages should be removed from physical memory and written to secondary storage when space is needed. Virtual memory provides advantages like allowing processes to exceed physical memory limits and improving performance when only parts of programs are actively being used. However, it can reduce performance and system stability when disk access is frequently required.