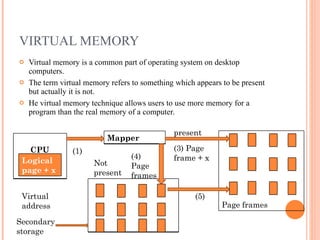
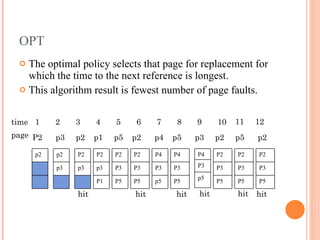
Virtual memory allows a computer to use more memory (called the address space) than is physically installed in the system (the memory space) by storing rarely used data on disk. When data is needed, it is moved back into memory. This allows for multiprogramming and for individual programs to be larger than physical memory. Common page replacement algorithms that determine what data to remove from memory and store on disk include first-in, first-out (FIFO), least recently used (LRU), and optimal (OPT) which removes the page not used for the longest time.