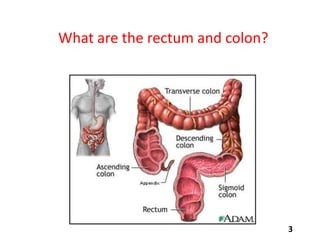
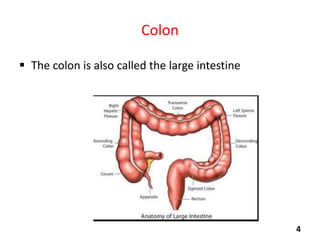
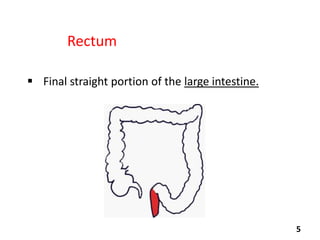
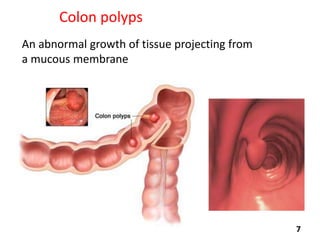
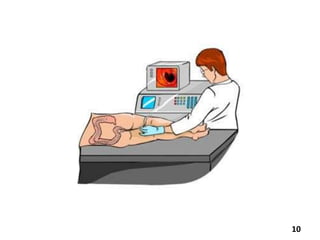
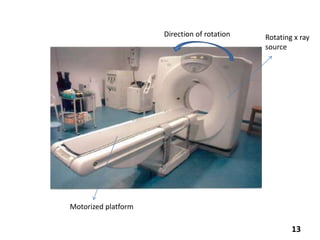
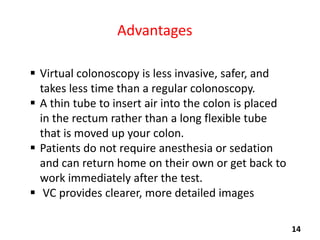
Virtual colonoscopy, also known as CT colonography, is a non-invasive medical imaging procedure that uses x-rays and computers to produce 2D and 3D images of the rectum and entire colon. It can detect polyps and other abnormalities. The colon and rectum are parts of the large intestine; the rectum is the final straight portion. Virtual colonoscopy is performed to screen for or follow up on colon cancer, investigate symptoms like abdominal pain or blood in the stool, and check for polyps. It has advantages over standard colonoscopy in being less invasive, safer, and allowing patients to return to normal activities sooner, but it cannot be used to biopsy or remove polyps and may miss some smaller polyps