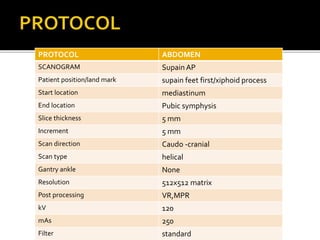
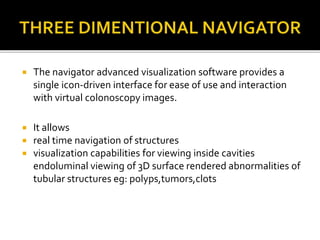
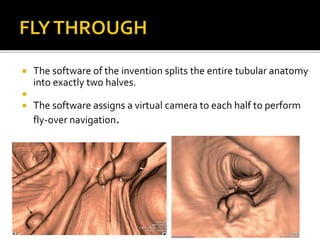
CT colonoscopy, also known as virtual colonoscopy, is a medical imaging procedure that uses x-rays and computers to produce two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of the colon without the need for invasive instrumentation. It can be used to evaluate the colon for polyp detection and colorectal cancer screening. The procedure involves inserting a thin tube to inflate the colon with air for better viewing as the patient lies on an examination table that passes through an x-ray scanner to produce cross-sectional images. A computer then combines these images to generate 3D pictures that can be viewed on a screen.