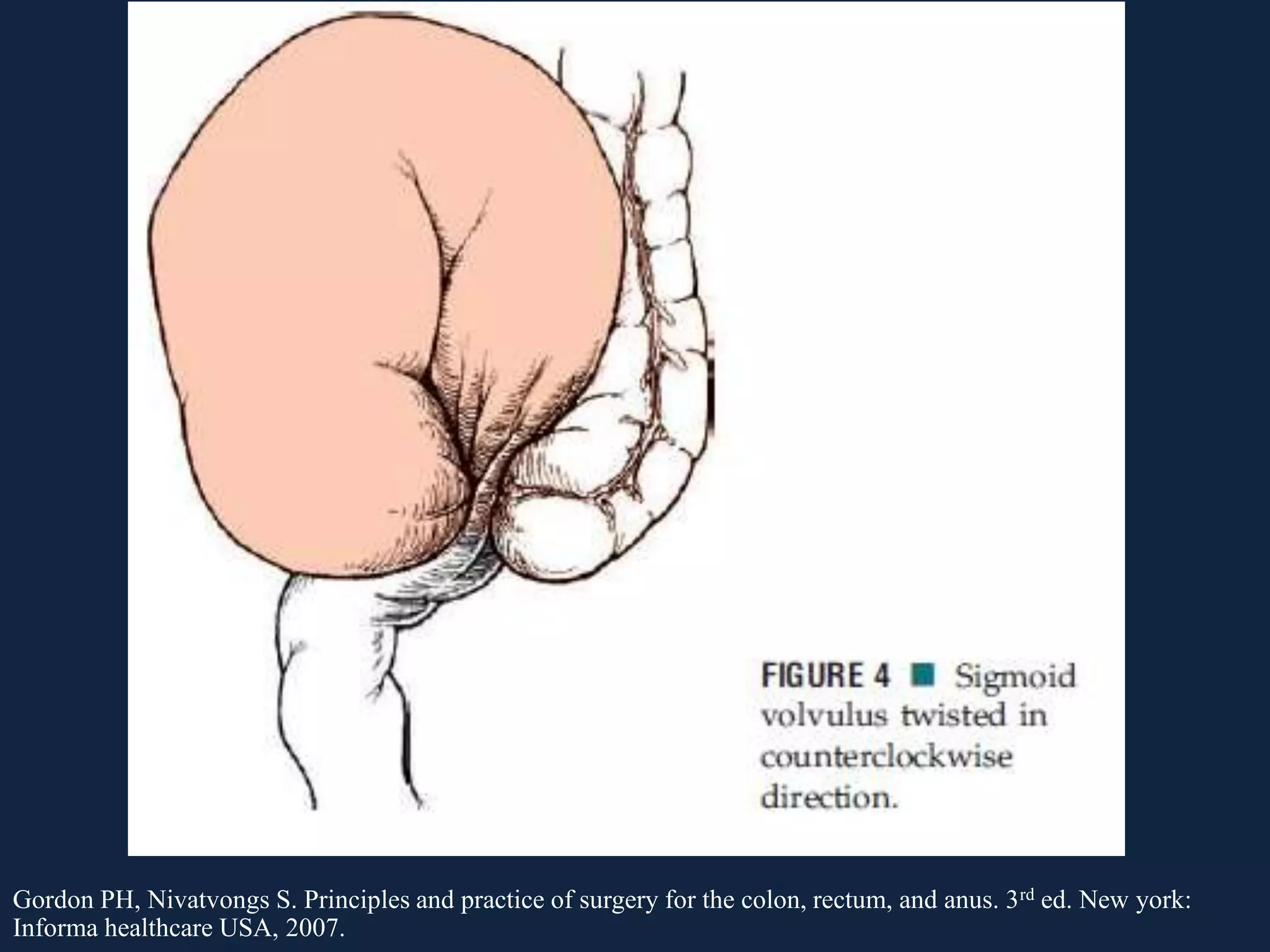
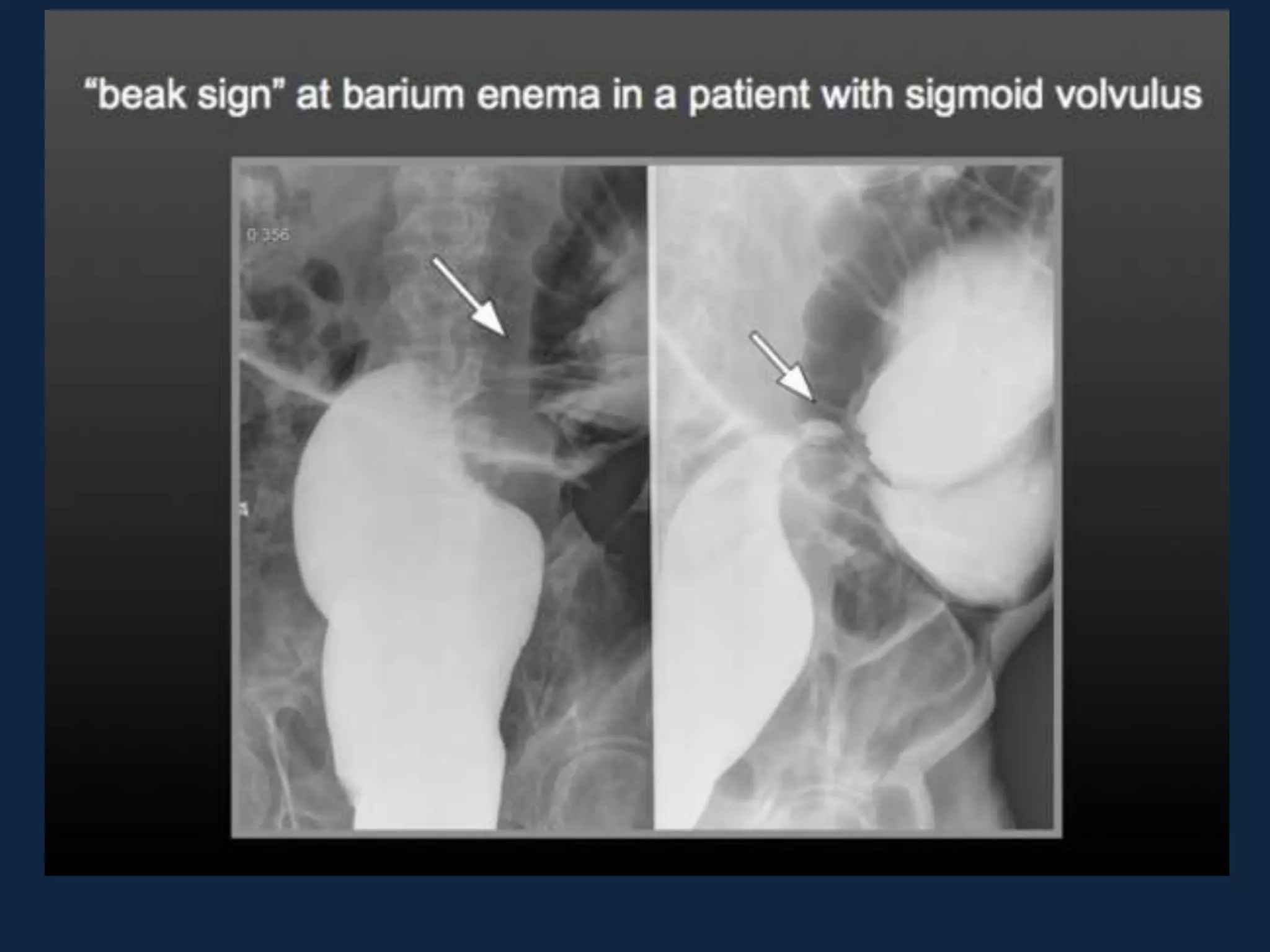
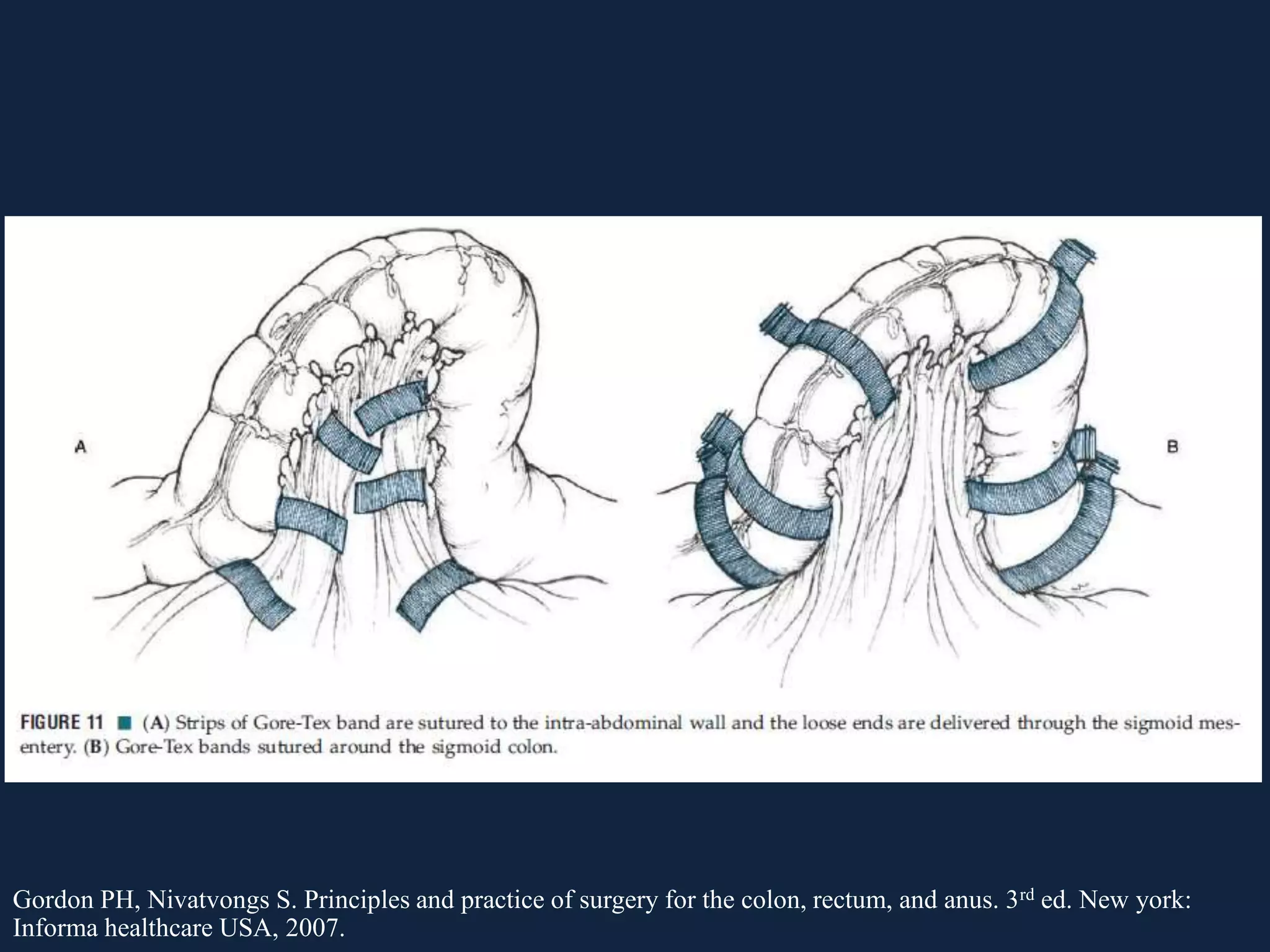
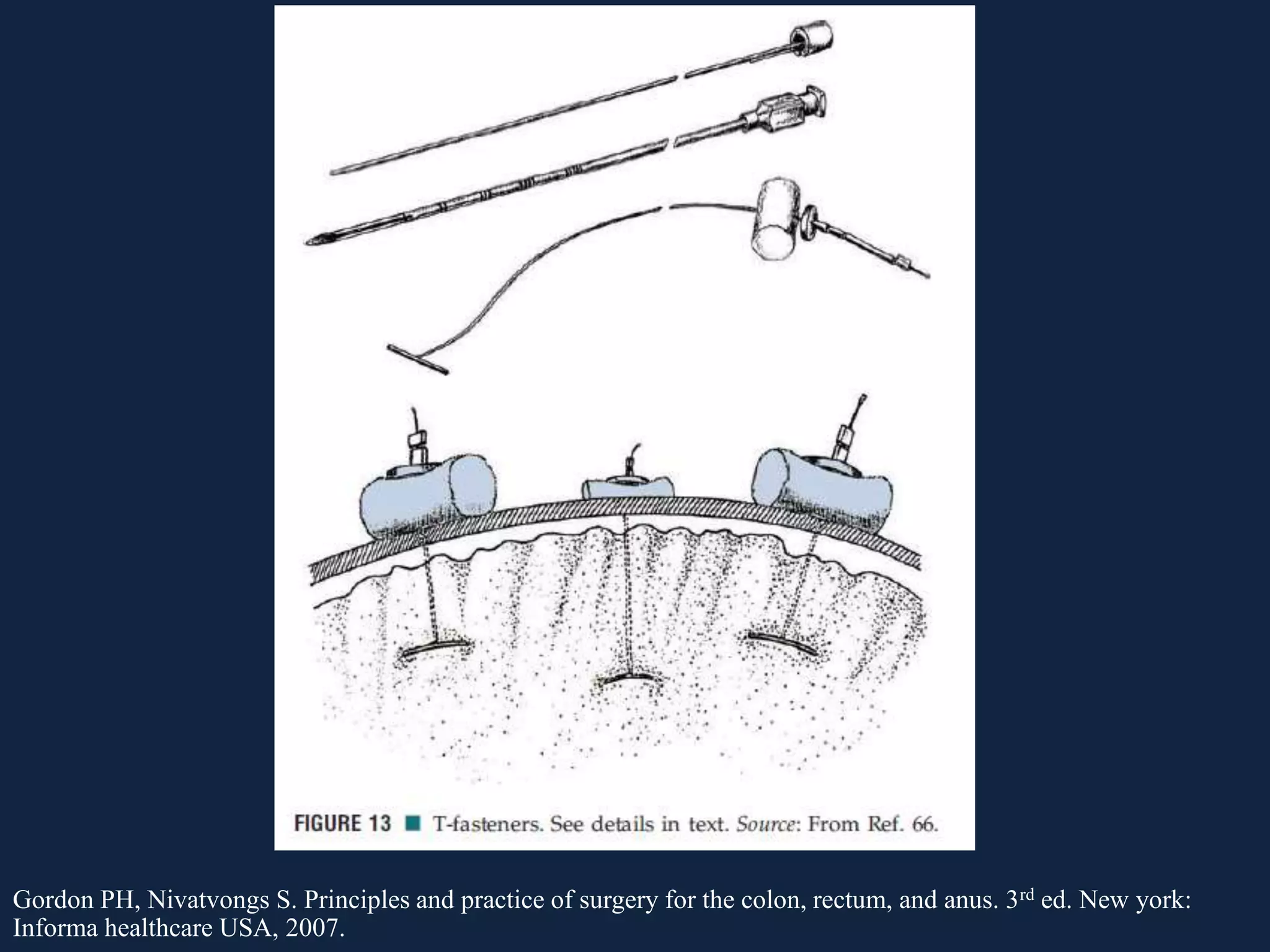
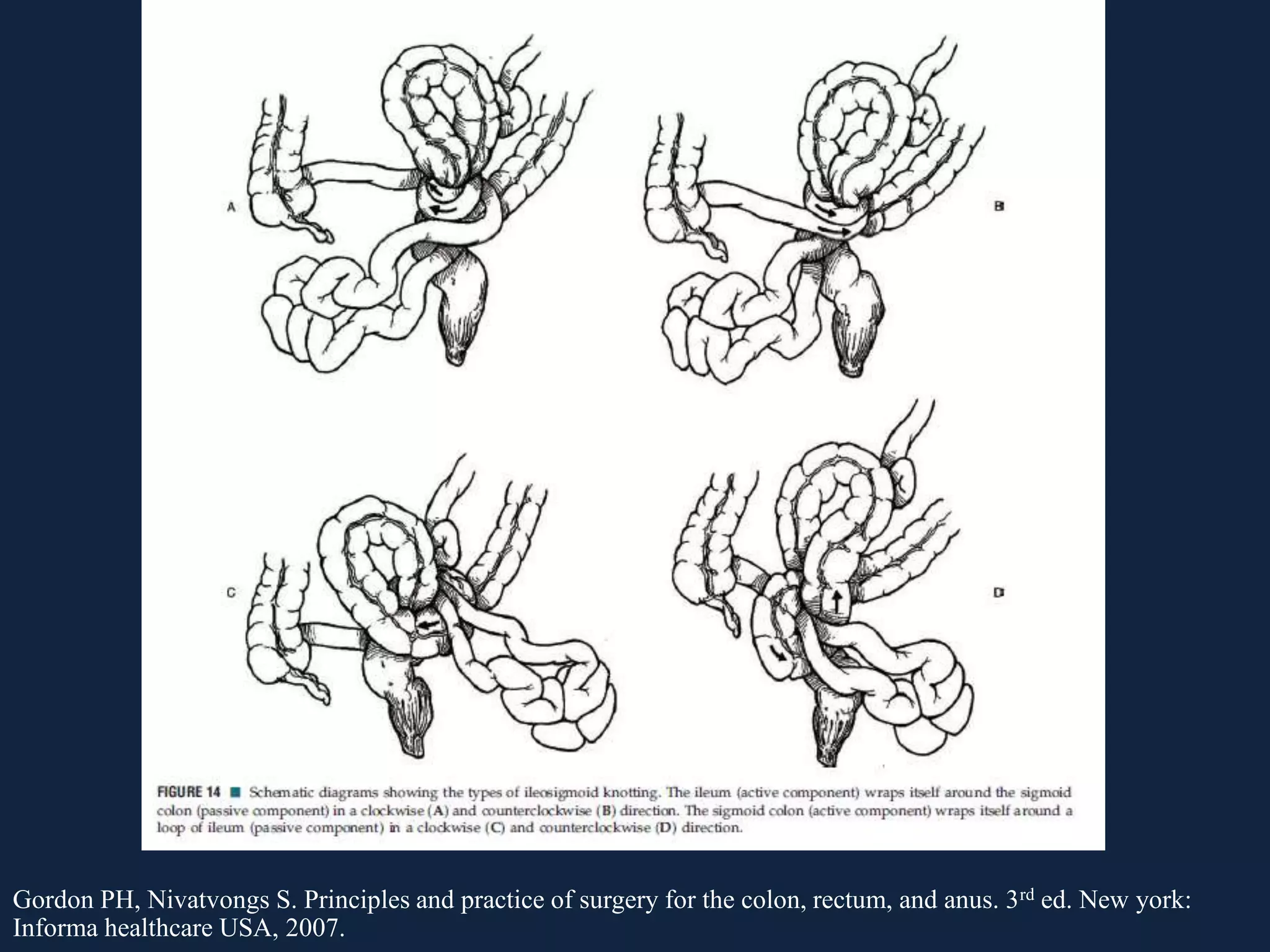
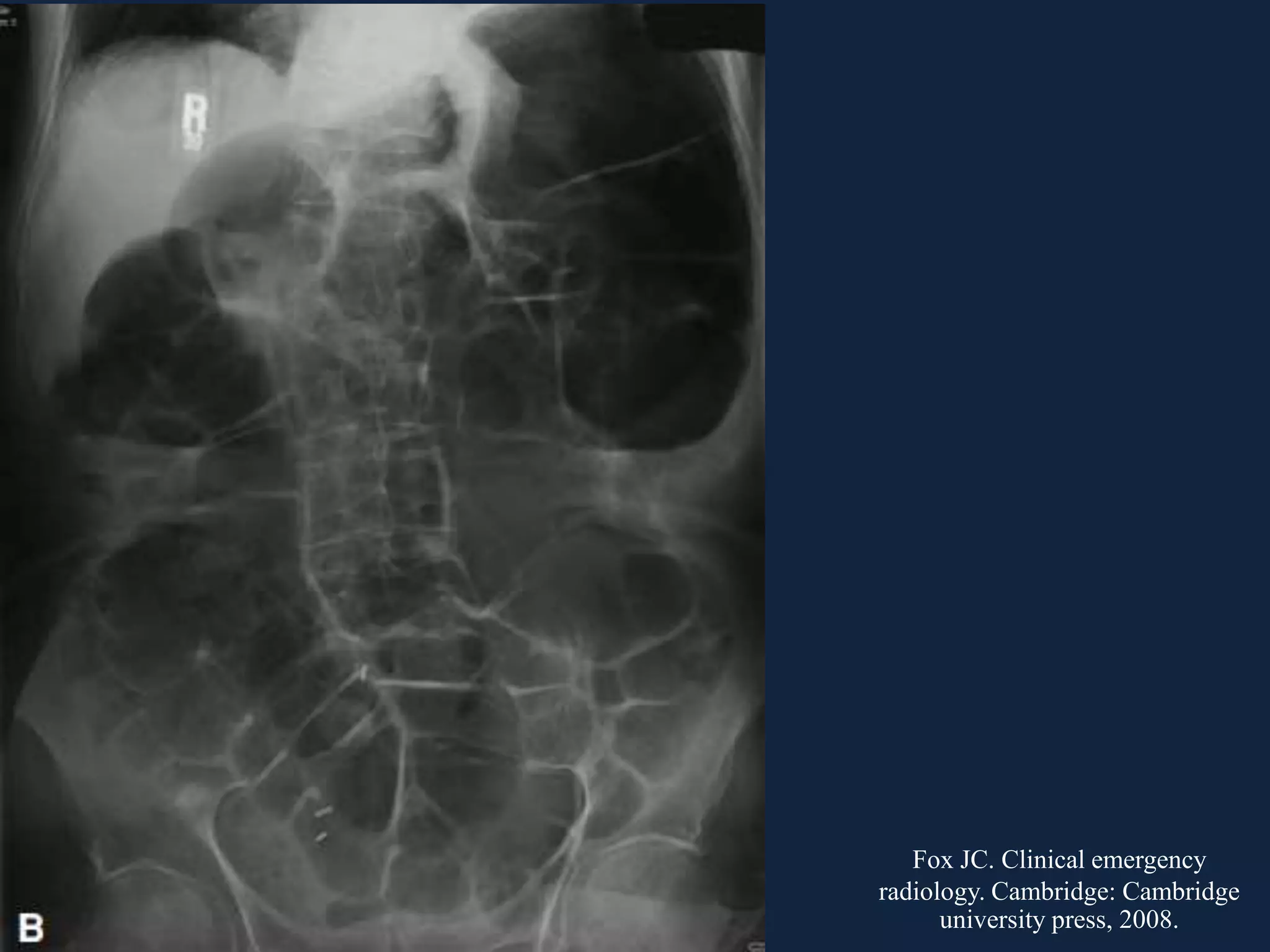
This document discusses various causes of large bowel obstruction including cancer, inflammation, volvulus, and Ogilvie's syndrome. It provides details on the diagnostic evaluation, imaging findings, and treatment options for partial versus complete, simple versus strangulating obstructions. The most common mechanical cause is colorectal cancer while the most common adynamic cause is acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. Treatment depends on the etiology and includes resection, stenting, decompression, and creation of a stoma.