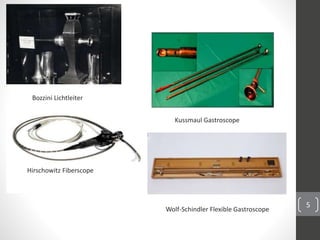
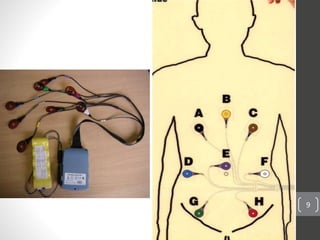
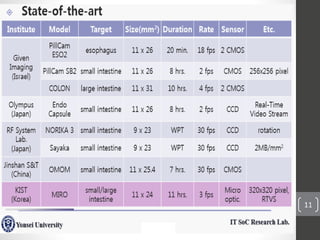
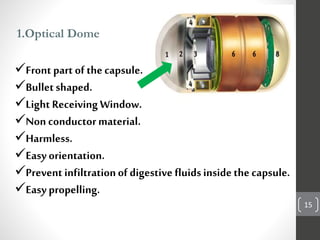
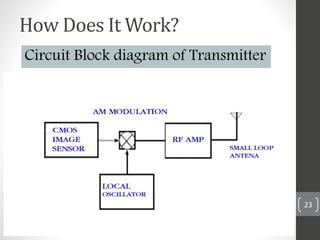
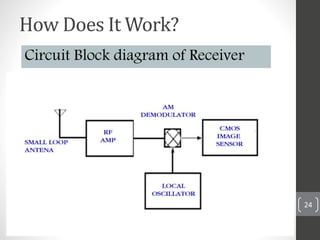
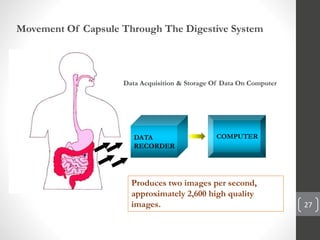
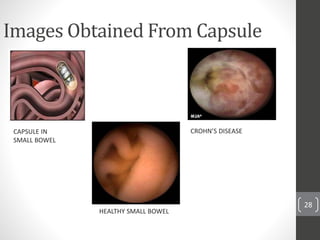
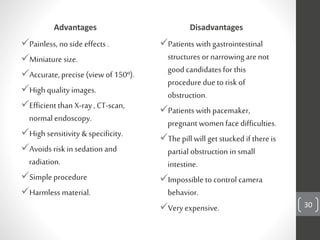
Capsule endoscopy is a medical procedure where a patient swallows a small capsule containing a camera. The capsule travels through the gastrointestinal tract taking pictures, which are transmitted to a data recorder worn by the patient. This allows physicians to examine the small intestine for conditions like bleeding, polyps, or inflammatory bowel disease. The capsule is painless, provides high quality images, and avoids risks of other imaging techniques. However, it cannot be controlled and may get stuck if obstructions are present. The document provides details on the history, components, procedure, uses, and advantages/disadvantages of capsule endoscopy.