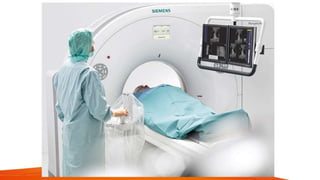
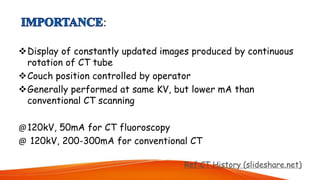
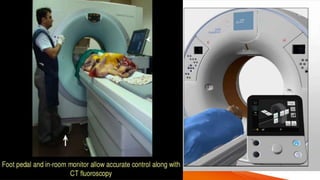
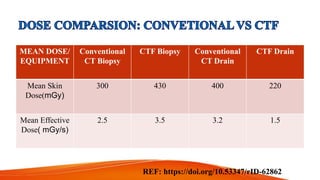
CT fluoroscopy combines the imaging capabilities of CT and fluoroscopy for real-time interventional procedures, offering continuous image updates and accurate guidance in biopsies and fluid drainages. Developed in 1993 and FDA approved in 1995, this technique utilizes advanced technology to reduce radiation exposure and procedure time while enhancing operational efficiency. However, it requires careful management of equipment and may present challenges such as noise-induced image quality and limited scanning range.