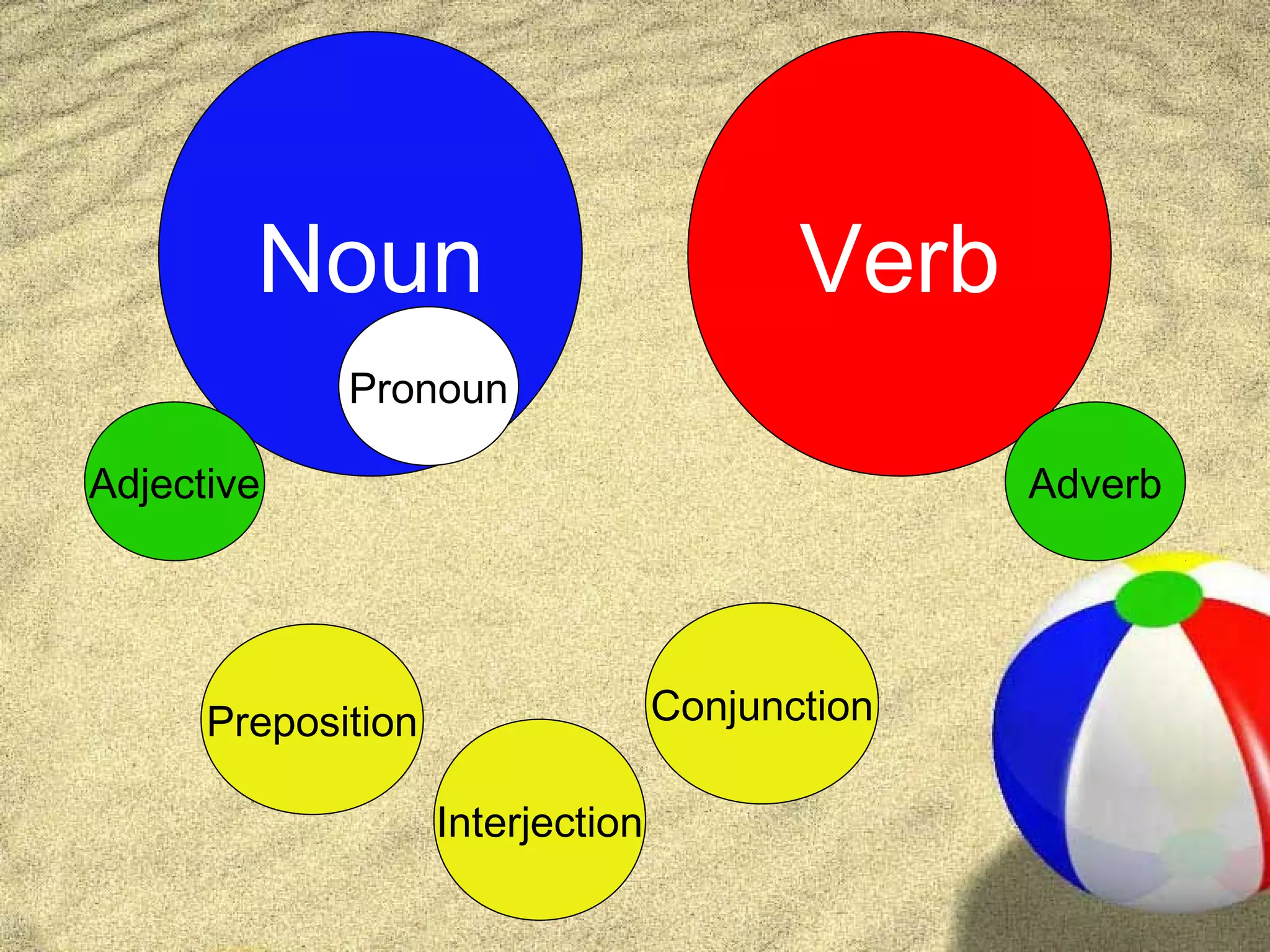
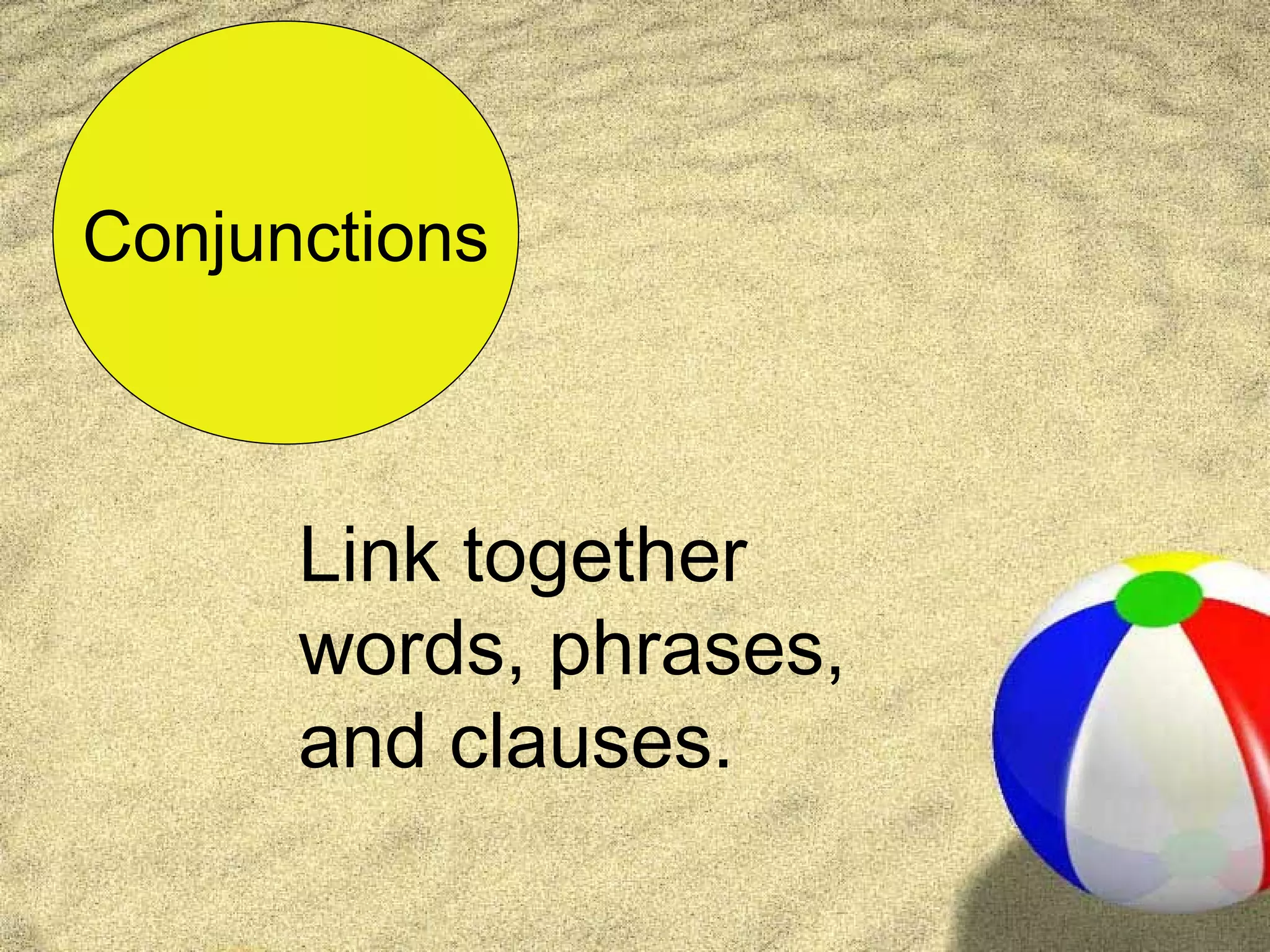
The document provides an overview of English grammar, outlining the 8 parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It defines each part of speech and provides examples. Key details include defining nouns as people, places, things, or ideas, verbs as action or linking words, adjectives as descriptive words, and prepositions showing relationships between words.