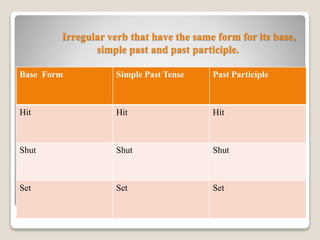
This document discusses different types of verbs including transitive verbs, intransitive verbs, regular verbs, and irregular verbs. Transitive verbs take a direct object, such as "kick the ball," while intransitive verbs do not take a direct object and describe actions like "run." Regular verbs form their past tense and past participle by adding "-ed" or "-d," but irregular verbs do not follow this pattern and must be memorized. Examples of regular and irregular verb conjugations are provided.