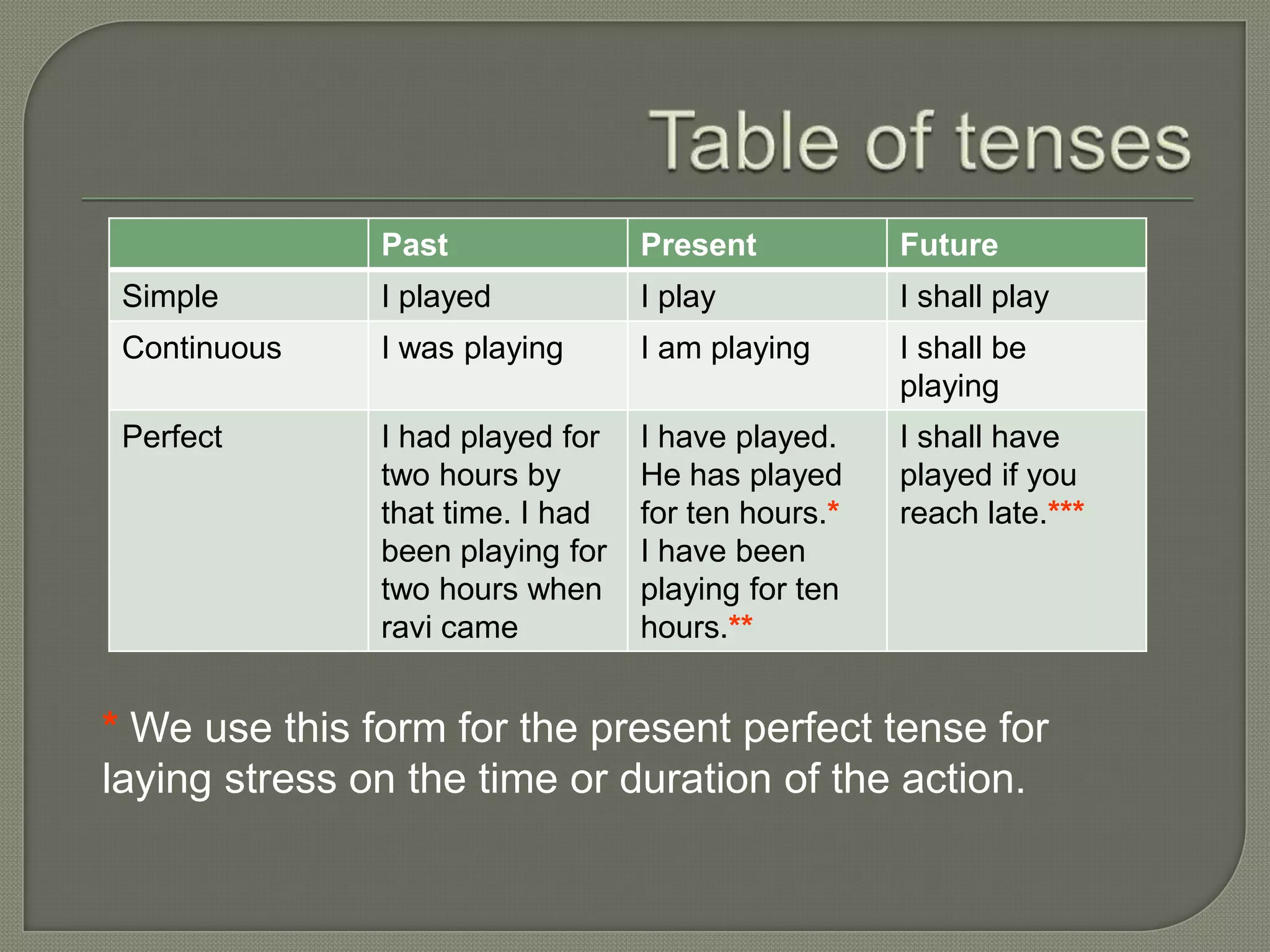
The document discusses the different tenses in English - past, present, and future - and their simple, continuous, and perfect forms. It provides examples for each tense, explaining how they are used to indicate the time and type of action being described. Specifically, it outlines 12 tenses total based on combining time (past, present, future) with type (simple, continuous, perfect).