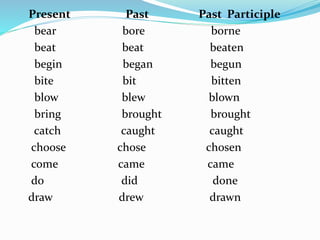
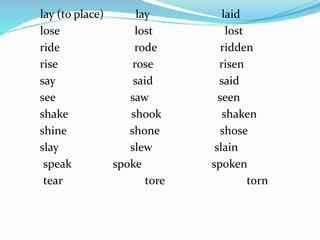
This document discusses verb tenses and types of verbs in English grammar. It explains the simple present, past, and future tenses and how they are formed. It also covers the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect tenses. Modal verbs like can, could, should and must are described. The uses of do, does and did as auxiliary verbs are provided. Finally, it discusses irregular verbs and their past and past participle forms.