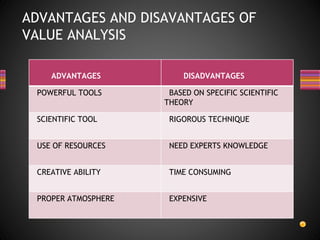
The document discusses vendor rating, which is a formal system used by firms to evaluate the performance of vendors who provide contingent labor or supplies. It describes several factors considered in vendor ratings like pricing, quality, delivery, and various techniques used to rate vendors. These include categorical plans, weighted point methods, cost ratio methods, and checklists. The benefits of vendor rating include providing feedback, facilitating communication, controlling vendors, and building partnerships. Value analysis is also discussed as a method to identify unnecessary costs and achieve functional objectives like durability most economically. It aims to save money while maintaining quality.