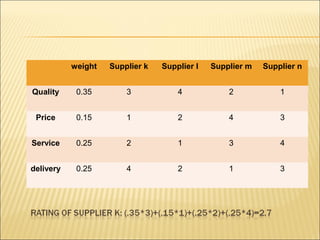
The document discusses the importance of the vendor selection process for organizations. It outlines the key steps in the supplier selection process, including evaluating needs, gathering a pool of vendors, interviewing vendors, and selecting an evaluation method. Several supplier evaluation criteria are examined, such as financial health, expertise, and risk factors. Finally, the document describes different supplier evaluation methods like the categorical method, weighted point method, and cost-ratio method and provides an example problem demonstrating the weighted point method.