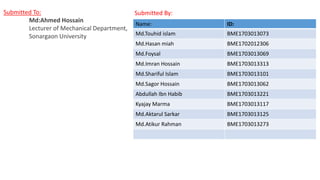
This document contains a presentation on vector analysis and matrices submitted by mechanical engineering students at Sonargaon University. It includes definitions of vectors, types of vectors, vector operations of addition, subtraction, dot product and cross product. It also defines different types of matrices, matrix operations of addition and subtraction, and scalar multiplication. Applications of vectors and matrices are discussed for calculating forces, velocities, and in cryptography to encrypt data for privacy.







![The above system of numbers, arranged in a rectangular array in rows and columns
and bounded by brackets , is called a matrix.
Various Types Of Matrices:
(a)Row Matrix: If a matrix has only one row and any number of columns, its called
row matrix. e . g
[2 7 3 9]
(b) Column Matrix: A matrix, having one column and any number of rows, its called
column matrix. e . g
1
2
3
1
(C) Null Matrix/Zero Matrix: Any matrix, in which all the elements are zeros, is called
a zero matrix/ null matrix. e . g
0 0 0
0 0 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/math-180728145811/85/Vector-analysis-matrix-9-320.jpg)





