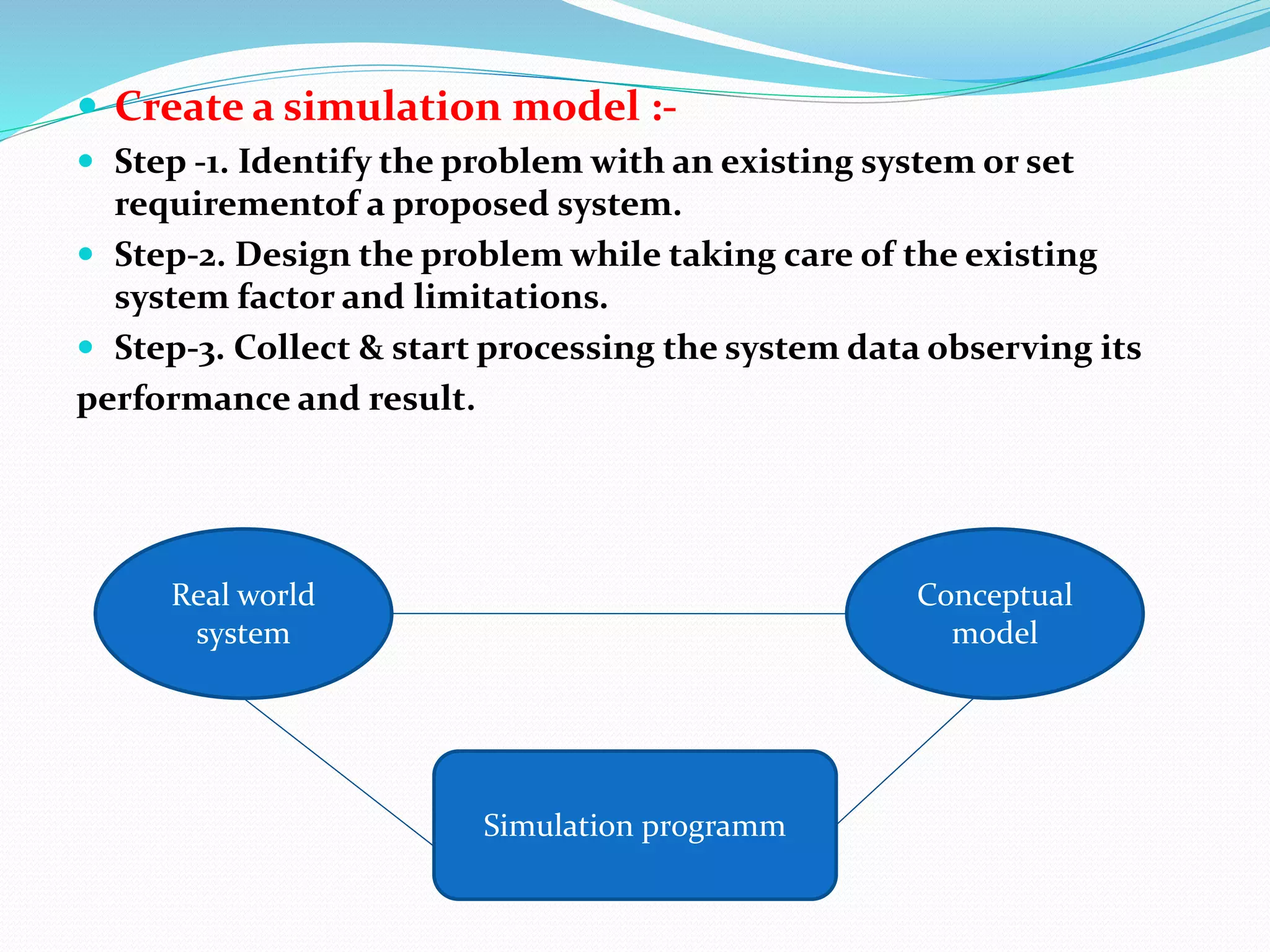
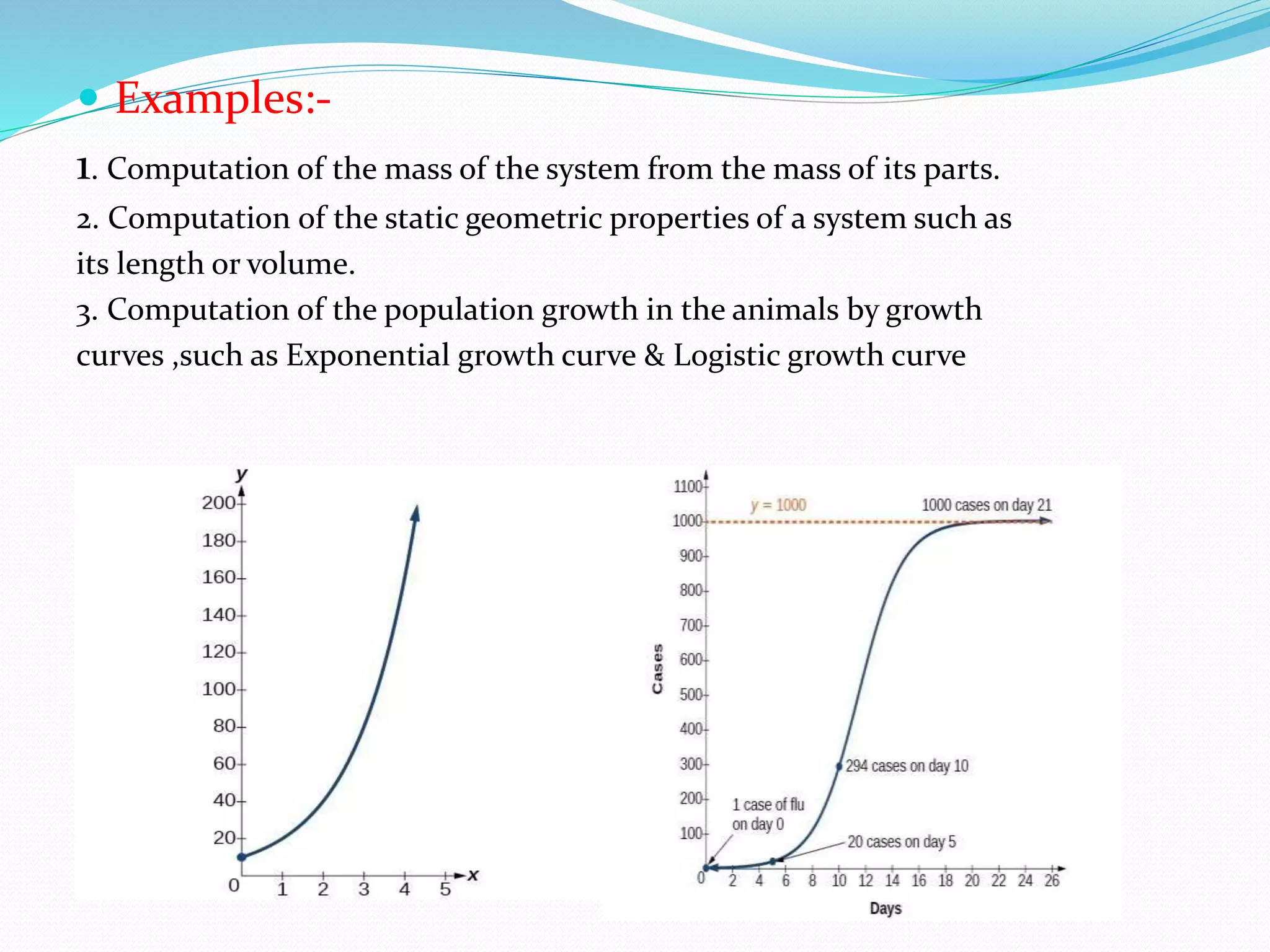
This document provides an overview of mathematical modeling. It defines mathematical modeling as using mathematical concepts and language to describe a system. The summary explains that mathematical modeling involves converting a real-world problem into a mathematical problem through interpretation, then deriving a mathematical solution and interpreting it back in terms of the real problem. It also discusses the key components, properties, types and examples of mathematical modeling, as well as its merits in fields like epidemiology, economics, and engineering. However, it notes that models are simplifications and may not replace reality.