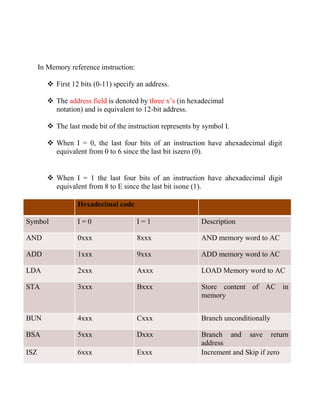
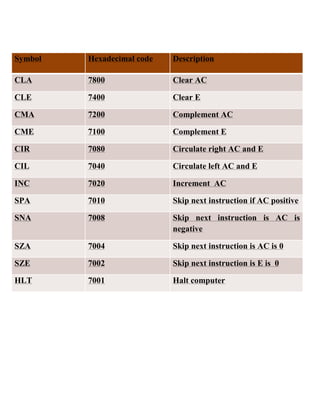
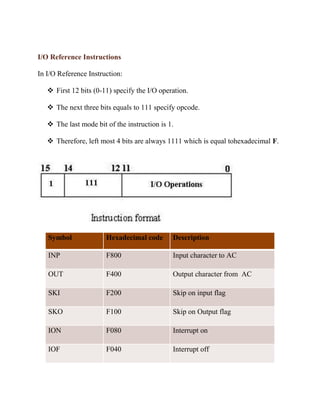
The document discusses different types of instruction formats used in computers. There are three main types: memory reference instructions, register reference instructions, and I/O reference instructions. Memory reference instructions use bits to specify an operation code and memory address. Register reference instructions use bits to specify register operations. I/O reference instructions use bits to specify input/output operations.