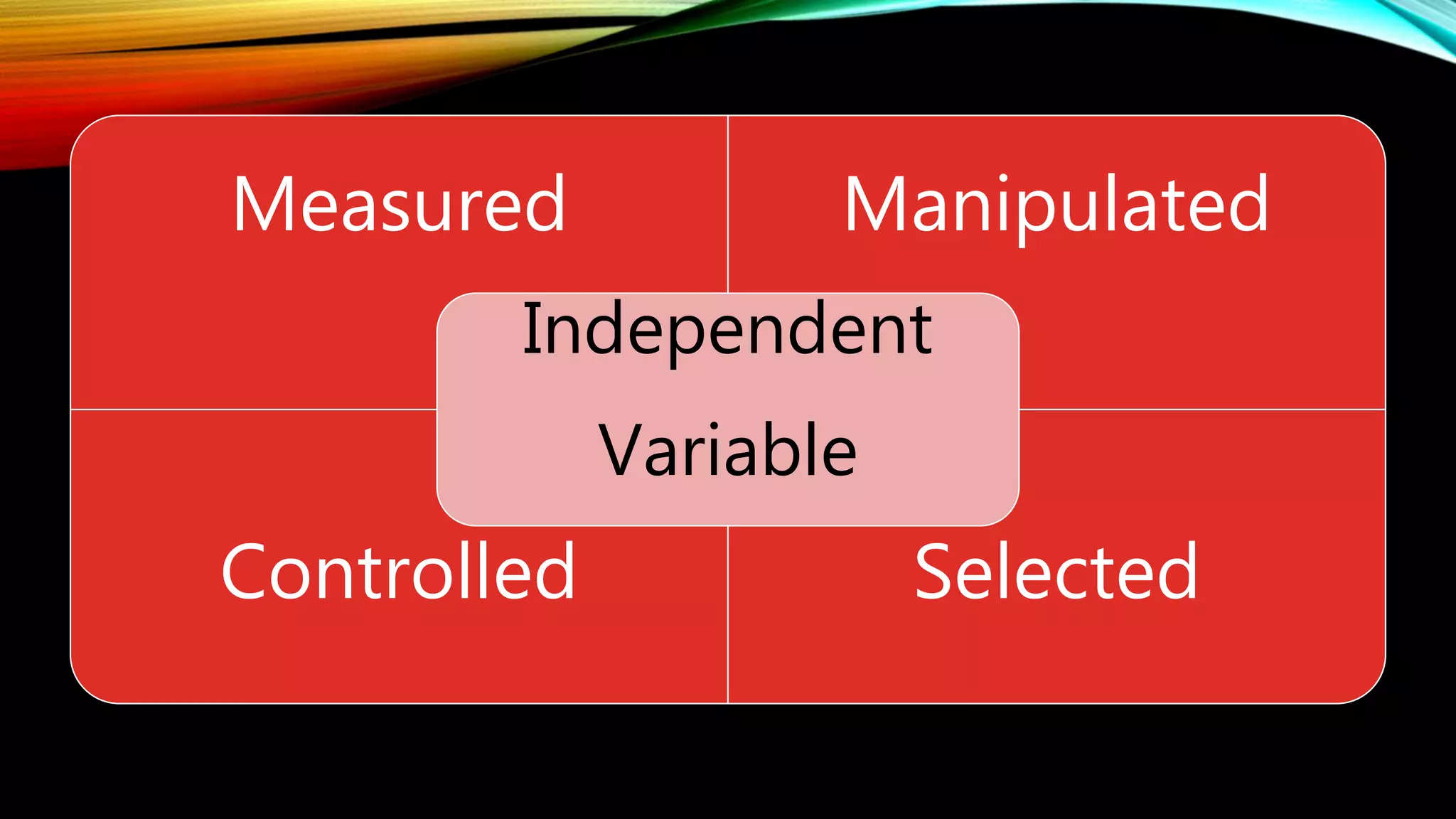
The document discusses different types of variables that can be studied in educational research. It defines an independent variable as a variable that is manipulated by the researcher to determine its effect on a dependent variable. A dependent variable is the observed response or outcome measured to assess the impact of changes to the independent variable. The document also discusses moderator variables, which modify the relationship between independent and dependent variables, and control variables, which are managed to neutralize their effects. Intervening variables can also impact the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Identifying key variables is important for focusing the research and defining how data will be collected and measured.