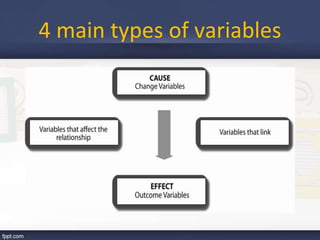
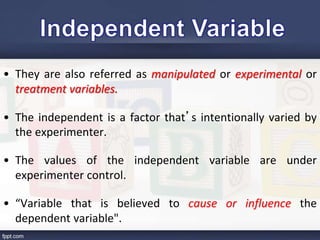
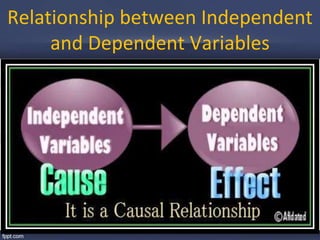
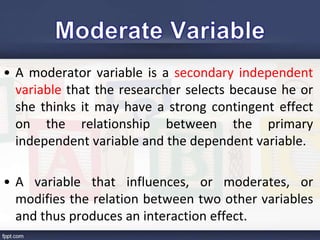
This document discusses key concepts related to variables in research:
- It defines different types of variables including dependent, independent, moderator, intervening, and controlled variables. Examples are provided for each.
- It also discusses operational definitions, manipulated variables, and controlled variables. Operational definitions specify how variables will be measured or observed. Manipulated variables are those intentionally varied by researchers, while controlled variables are kept constant.
- Key terms are defined concisely with relevant examples to illustrate different types of variables and how they are used in research studies.