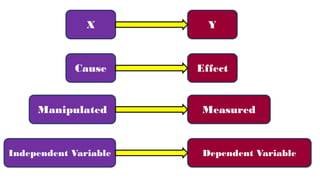
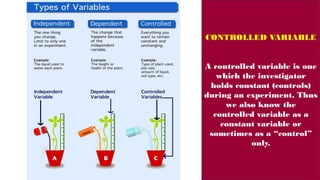
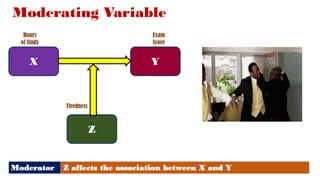
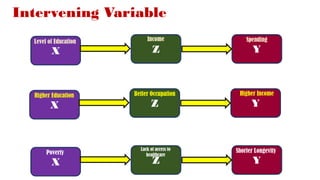
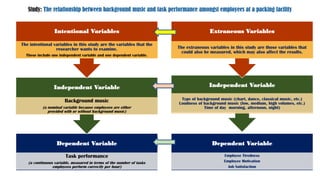
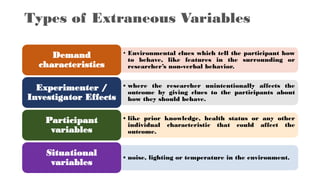
The document discusses various types of variables in research, including independent, dependent, and controlled variables, as well as confounding, mediating, and moderating variables. It explains how these variables can influence study outcomes, with examples related to education and employee performance. Additionally, the document covers extraneous variables, measurement types, and the concept of composite variables to illustrate how researchers can analyze complex concepts.