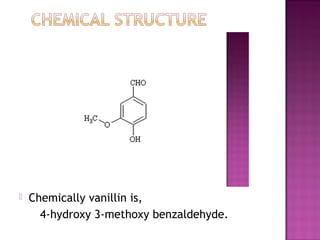
The document discusses the synthesis of semisynthetic derivatives of vanillin, a compound derived from vanilla pods, aimed at enhancing its biological activities. The study outlines experimental procedures and methodologies for synthesizing the derivatives and highlights their potential pharmacological uses, including analgesic and antibacterial properties. Additionally, it references literature that supports the idea that modifying the structure of compounds may improve their biological effectiveness.