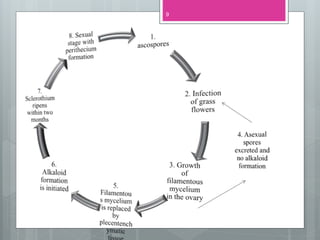
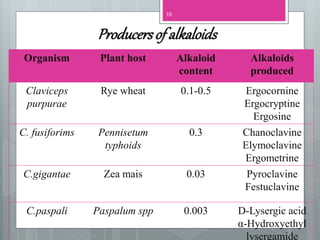
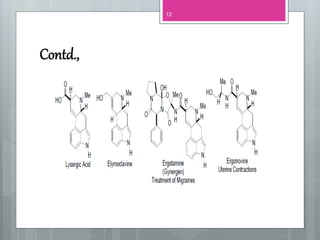
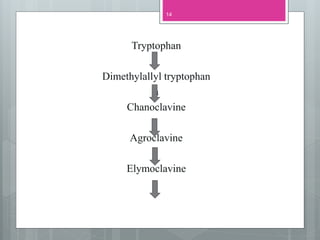
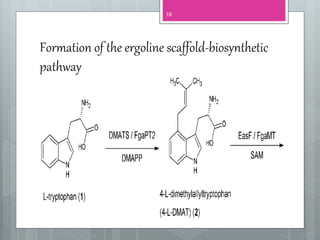
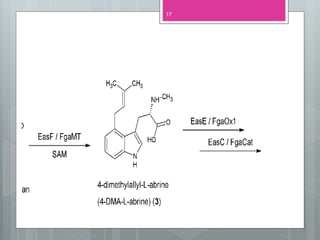
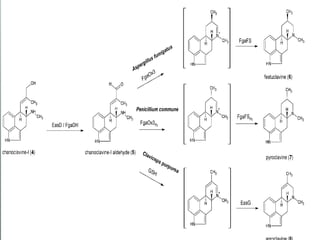
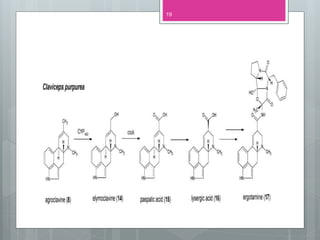
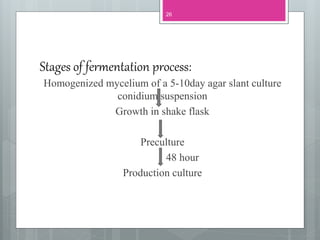
This document discusses ergot alkaloids, which are nitrogen-containing natural products produced by various fungi including Claviceps purpurae. It describes their chemical properties, occurrence, pharmacological effects, biosynthesis pathway, and methods of production. Key producers of ergot alkaloids are discussed, including C. purpurae which infects rye and produces ergometrine. The biosynthesis pathway involves the formation of the ergoline ring system from tryptophan. Methods of commercial production include culture of fungi on host plants or in submerged culture using processes like surface culture or immobilized cells. Regulation of alkaloid production in fermentation is also covered.