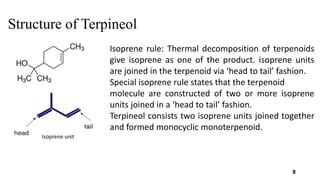
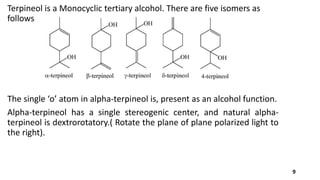
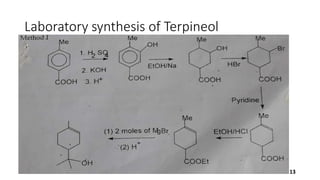
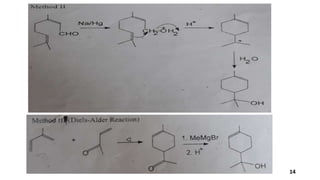
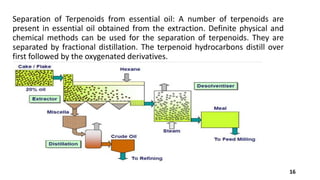
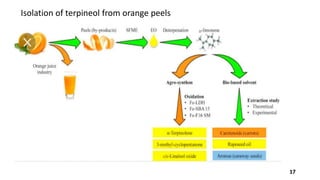
Terpineol is a natural terpenoid alcohol found in various plants, contributing to their fragrance and having several biological properties including antibacterial and antioxidant activities. It is primarily used in the perfume and cosmetics industries and has medicinal applications due to its diverse biological effects. The document details the structure, functions, applications, and methods of synthesizing and isolating terpineol.