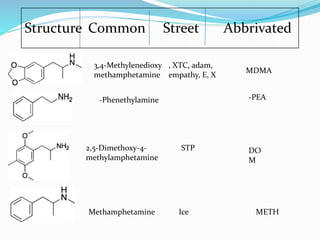
The document discusses designer drugs, which are substances created to mimic the effects of illegal drugs but evade controlled substance laws. It defines designer drugs and explains that they have similar psychotropic effects to illegal drugs, are not FDA approved, and are produced underground. The document then summarizes several common designer drugs like GHB, opioids, amphetamines, cannabinoids, and PCP, outlining their structures, street names, effects, and risks. It notes that designer drugs pose health hazards since their dosages are unknown.