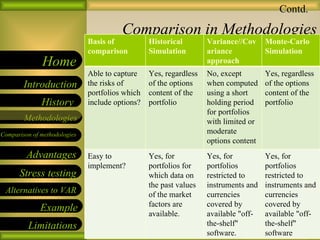
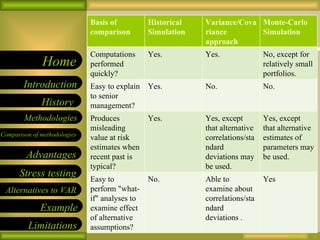
Value at Risk (VAR) is a risk management measure used to calculate potential losses over a given time period at a specified confidence level. There are three key elements - the level of loss, time period, and confidence level. For example, there is a 5% chance losses will exceed $20M over 5 days. VAR does not provide information on potential losses above the VAR level. There are three main methodologies used to calculate VAR - historical simulation, variance-covariance, and Monte Carlo simulation. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of implementation and ability to capture risk.