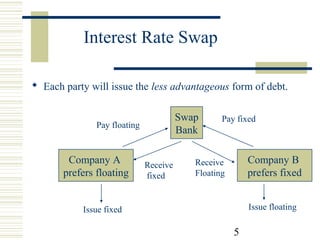
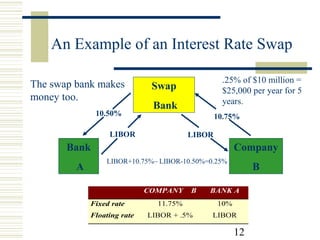
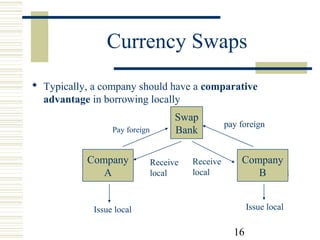
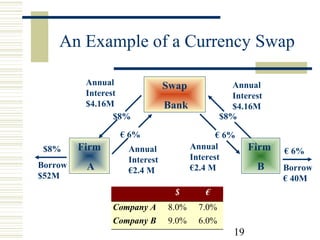
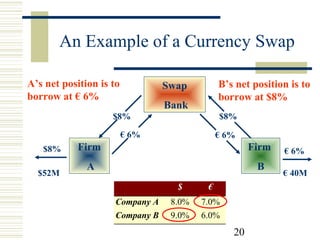
Currency and interest rate swaps allow companies to exchange interest rate and currency cash flows to hedge risks. Interest rate swaps exchange fixed and floating rate payments in the same currency. Currency swaps exchange interest payments in different currencies to fund projects abroad. Swap banks facilitate these exchanges and make markets in standard swaps, earning small spreads. Swaps benefit all parties by allowing each to borrow in their preferred currency or rate.