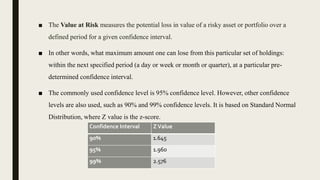
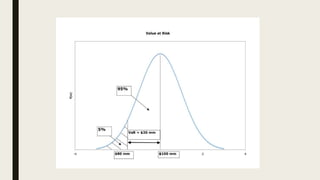
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical technique used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm, portfolio, or position over a specific time frame. It aims to quantify, with a single number, the maximum potential loss that could occur over a given time period at a given confidence level. There are different approaches to calculating VaR such as variance-covariance, historical simulation, and Monte Carlo simulation. VaR is widely used by banks and other financial institutions to monitor and control their risk exposure and capital adequacy. However, it does have some weaknesses as the results can vary depending on the underlying assumptions and there are costs associated with maintaining a VaR system.