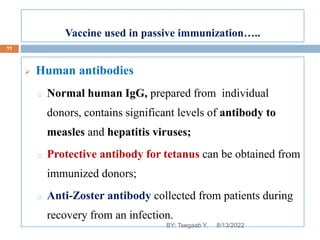
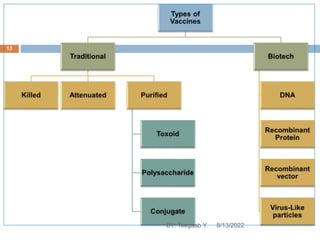
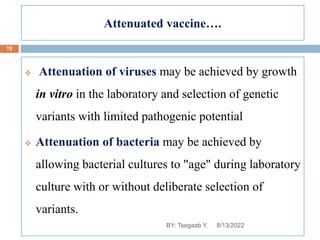
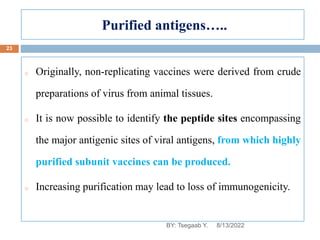
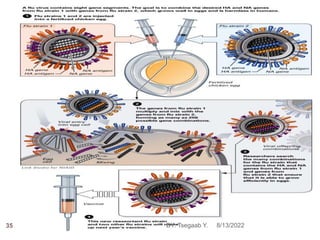
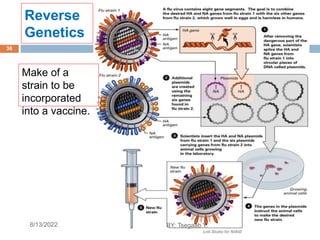
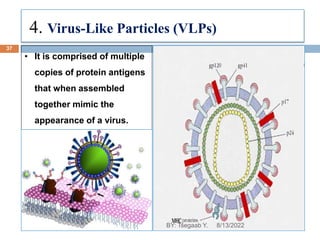
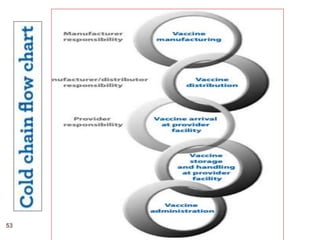
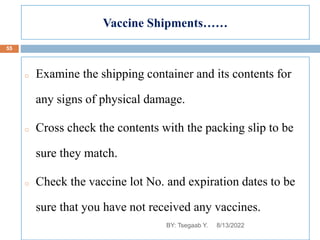
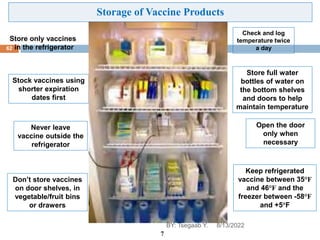
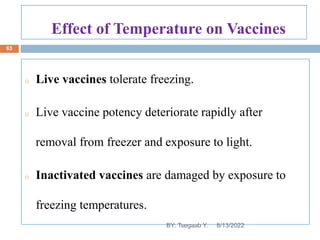
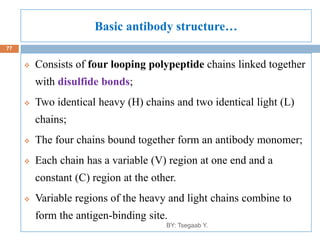
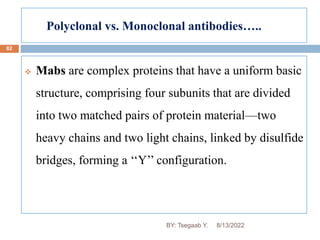
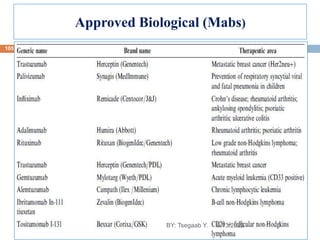
This document provides an outline and overview of vaccines. It discusses various topics related to vaccines including introduction to vaccines, modes of immunization, traditional vaccine types (killed pathogens, attenuated, purified antigens/toxoids), limitations of traditional vaccines, and biotech vaccines produced using recombinant DNA techniques (rDNA vaccines, recombinant proteins, recombinant vectors, virus-like particles). Production of vaccines using rDNA allows deletion of virulence genes while still stimulating immunity. The document is authored by Tsegaab Y. and covers these vaccine-related topics in detail across multiple pages.