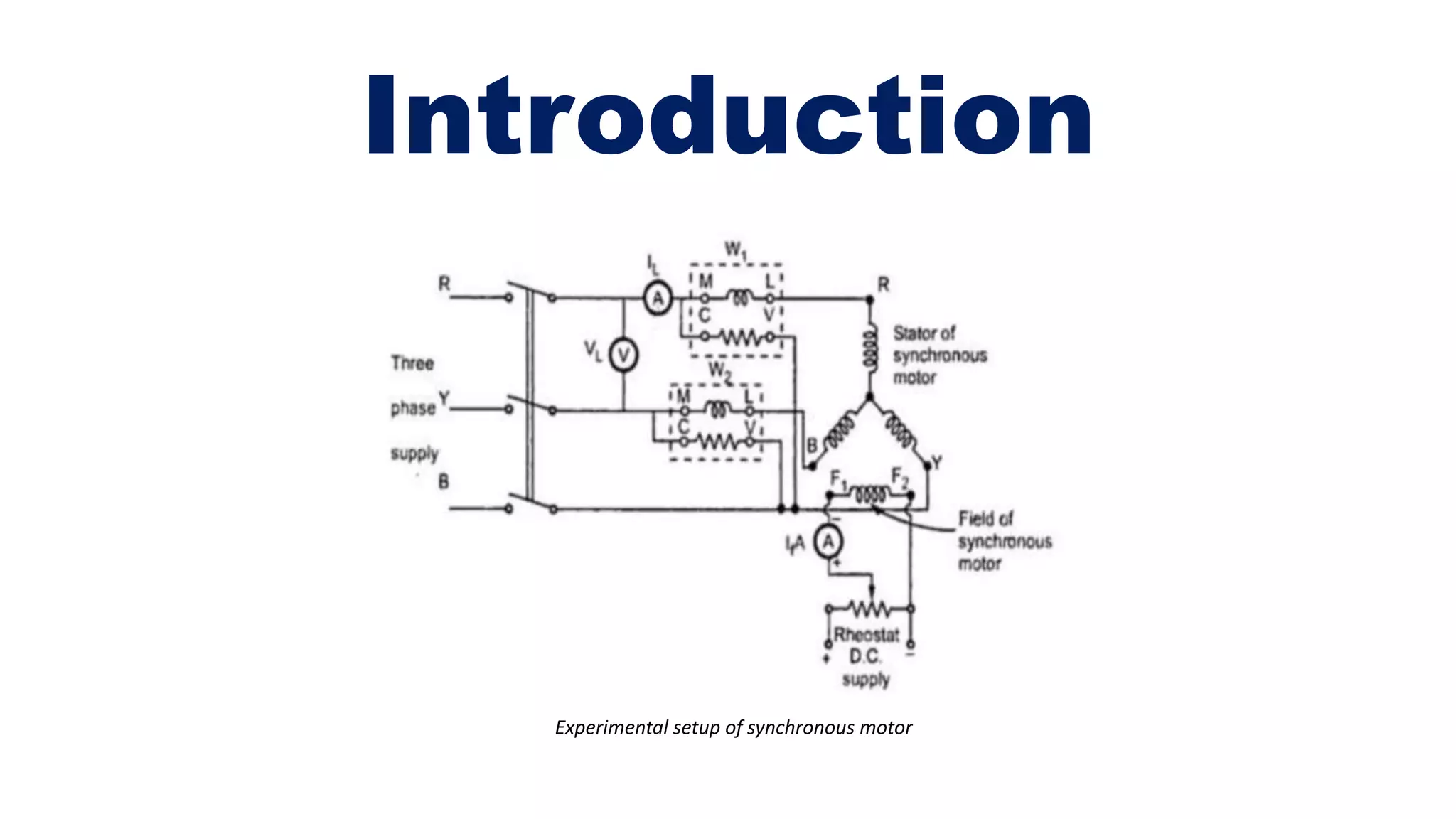
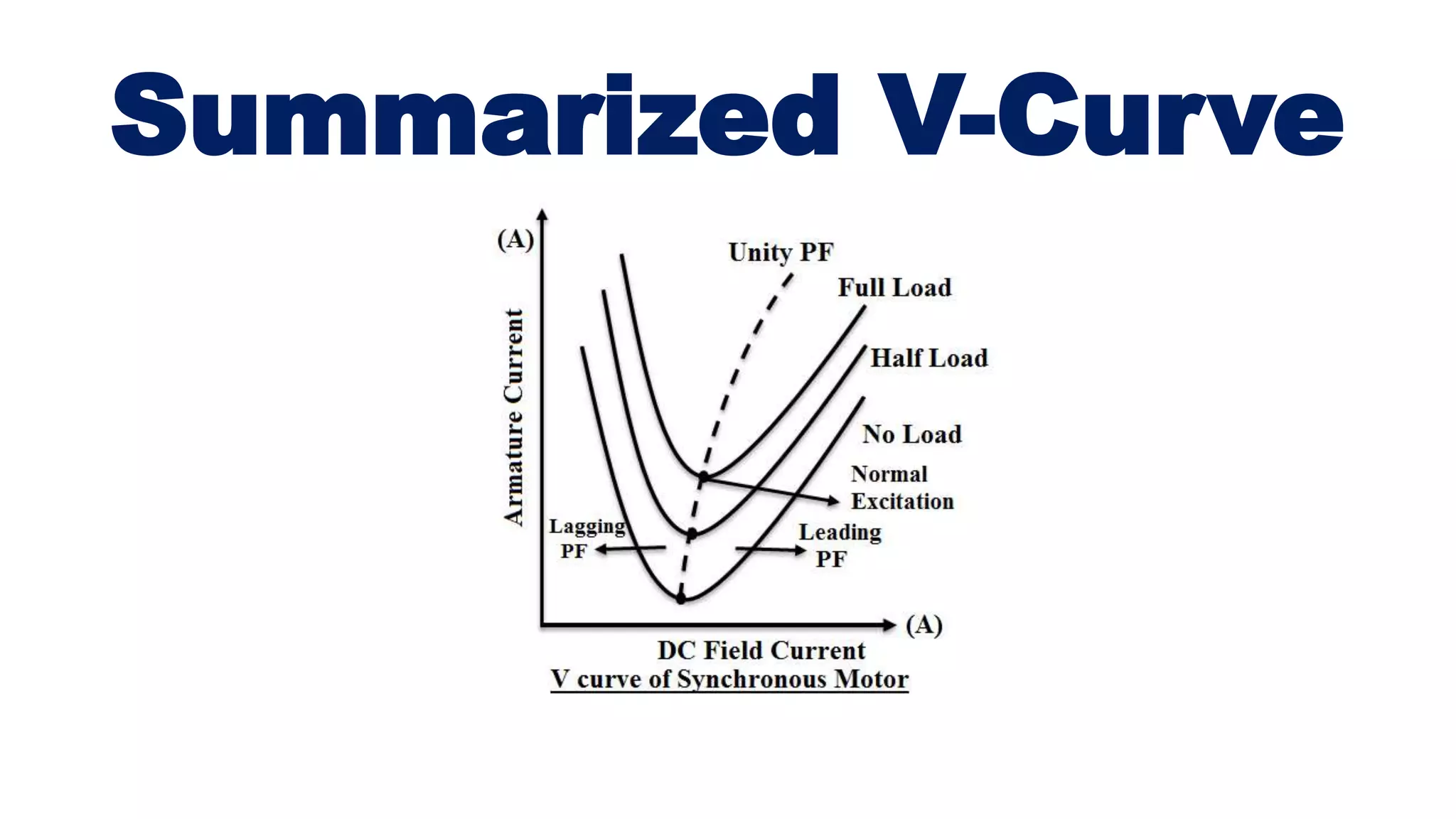
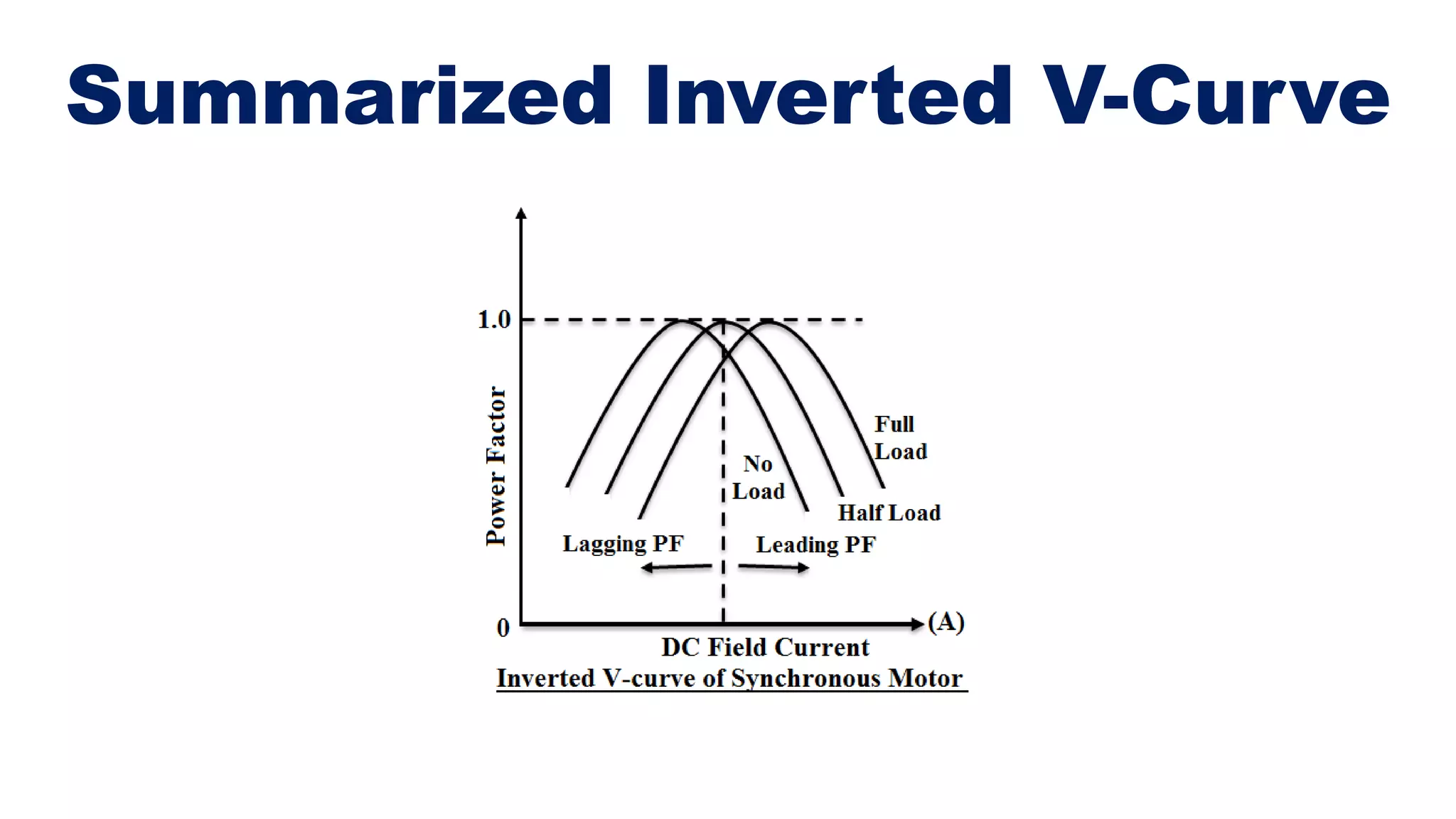
The document explains v-curves and inverted v-curves of synchronous motors, which are graphical representations of armature and field current relationships. It details how these curves indicate motor performance under various excitation levels, showing that power factor varies between lagging in under-excited conditions and leading in over-excited conditions. The analysis allows for insights into efficiency and current behavior, highlighting the importance of excitation in motor performance.