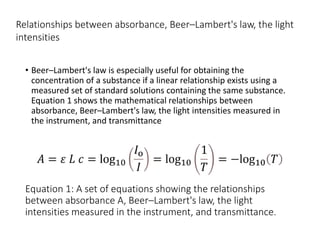
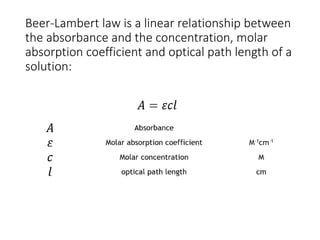
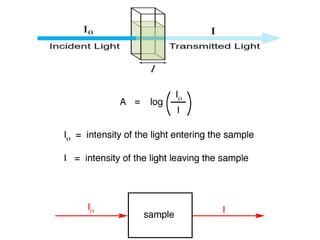
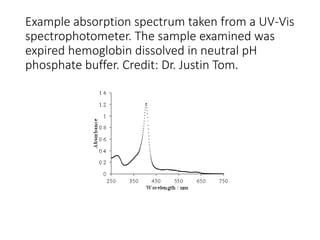
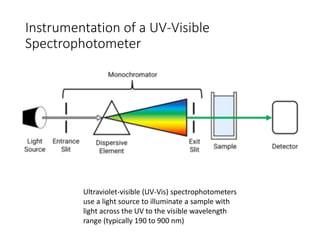
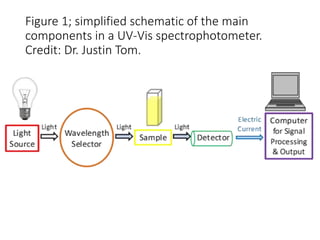
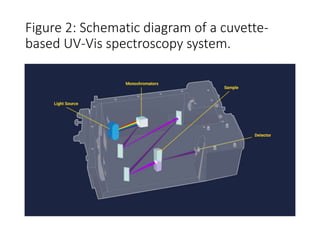
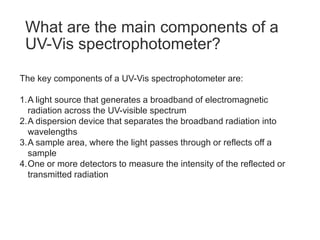
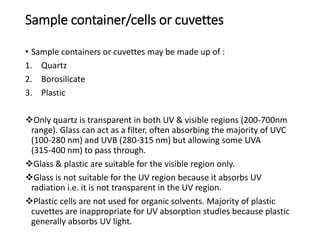
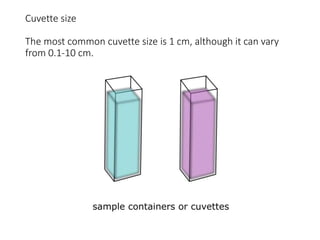
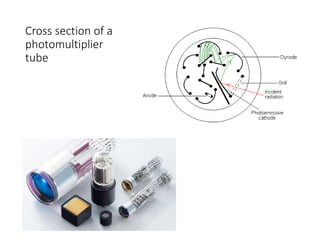
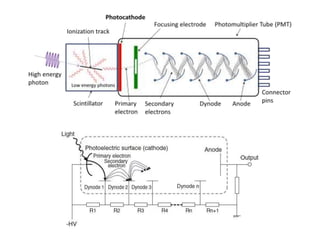
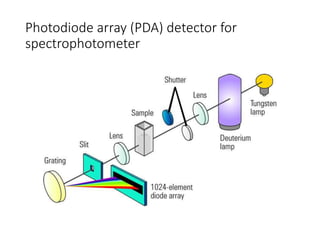
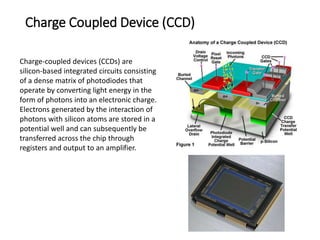
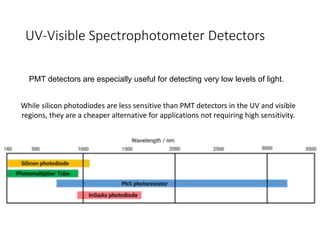
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy is an analytical technique that measures the amount of UV or visible light absorbed or transmitted by a sample. It provides information on the sample's composition and concentration. A UV-Vis spectrophotometer directs a light beam from a source such as a xenon lamp through a monochromator to isolate wavelengths, then through a sample and to a detector. It quantifies the light absorbed at each wavelength according to the Beer-Lambert law to obtain the sample's absorption spectrum and determine concentrations of absorbing substances in the sample.