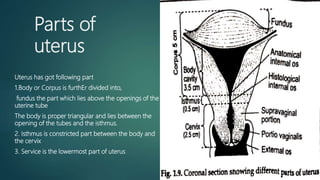
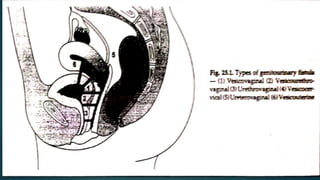
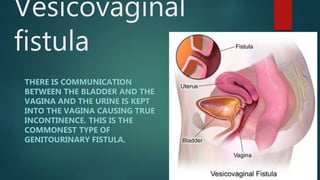
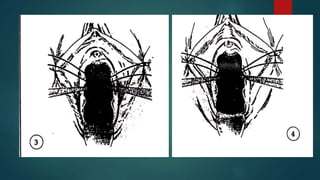
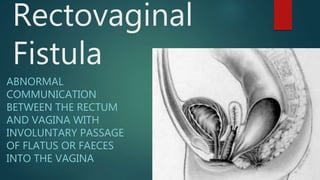
The document provides an extensive overview of genital fistulae, specifically focusing on genitourinary fistula and its types, causes, clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. It highlights the high incidence of such conditions in developing countries, predominantly resulting from obstetrical complications, and discusses various diagnostic tests and surgical interventions for managing fistulae. Additionally, preventive measures and postoperative care are emphasized to aid recovery and avoid future occurrences.