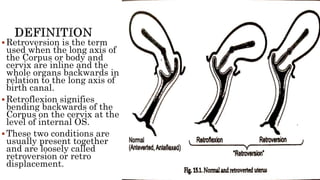
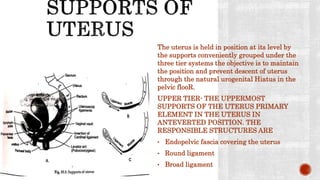
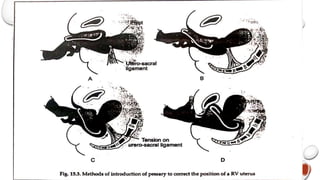
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomy and positioning of the uterus, detailing conditions such as retroversion and retroflexion, along with their implications for women's health. It discusses the support mechanisms for the uterus, developmental and acquired causes of displacement, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, including the use of pessaries and surgical corrections. The importance of correct diagnosis and preventive measures post-childbirth or abortion is emphasized to maintain uterine position and function.