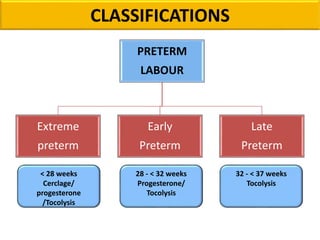
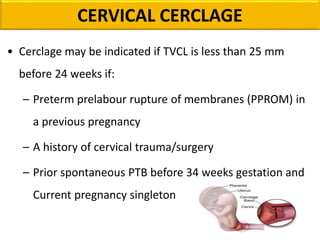
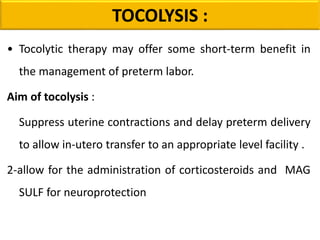
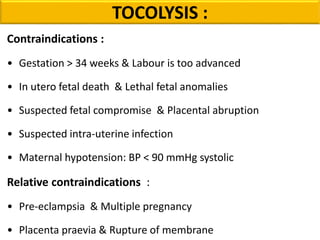
Preterm labor is defined as the onset of labor before 37 weeks of gestation. It is a leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality, affecting around 11.1% of births worldwide. Risk factors include low socioeconomic status, age under 18 or over 40, smoking, substance abuse, and previous preterm births. Diagnosis involves pelvic exams, ultrasound, fetal fibronectin testing, and cervical length screening. Management includes bed rest, tocolysis to delay delivery, corticosteroids to promote fetal lung maturity, antibiotics for infections, and magnesium sulfate which has both tocolytic and neuroprotective effects. Outcomes have improved with neonatal intensive care but prematurity remains a major challenge.