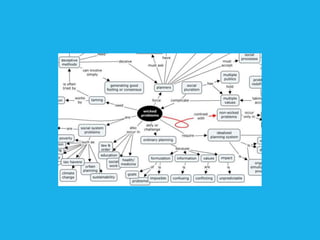
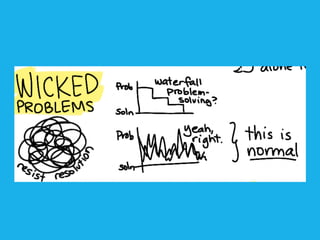
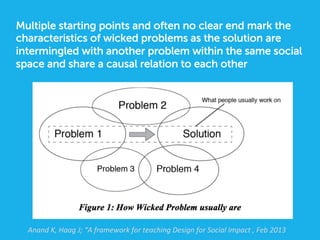
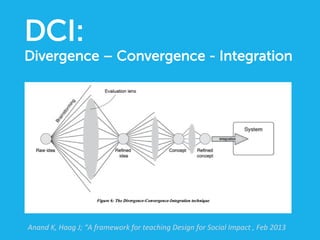
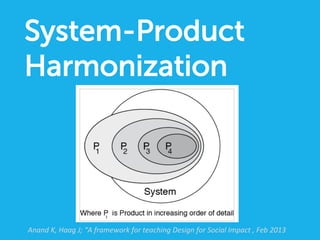
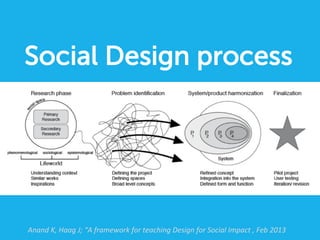
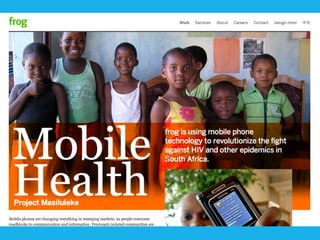
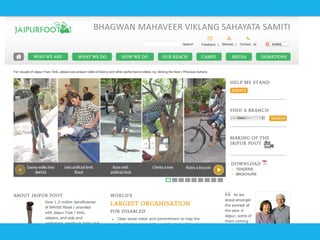
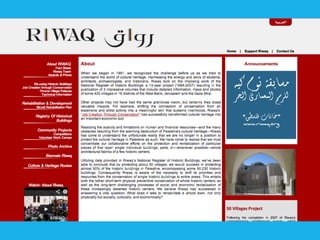
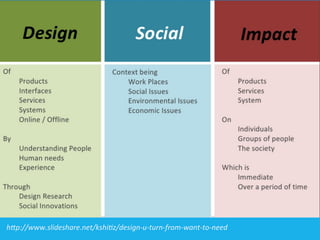
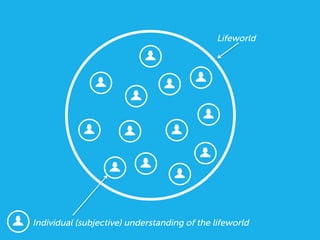
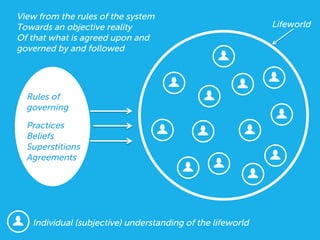
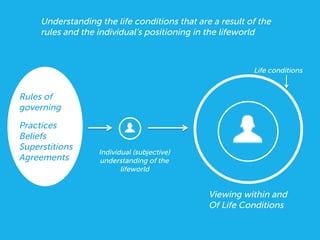
Social design aims to satisfy human needs and improve social quality by designing solutions that empower users. It involves understanding user lifeworlds from phenomenological, sociological, and epistemological perspectives to design with users' subjective experiences, social/material conditions, and life circumstances in mind. Social design addresses wicked problems which are difficult to define and solve due to their ill-formulated nature and conflicting stakeholder values. The social design process involves understanding contexts, identifying problems and user groups, analyzing information through user empathy, creating inclusive solutions that change systems rather than just produce outputs, and measuring both short-term tangible and long-term intangible impacts.



































![WICKED
PROBLEMS- Rittel Webber [ 1973]
With social design you would run into Wicked Problems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/socialdesignpresentation-130522000159-phpapp02/85/Social-Design-50-320.jpg)