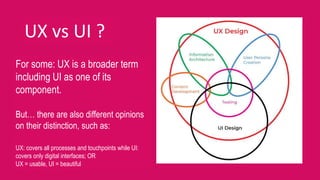
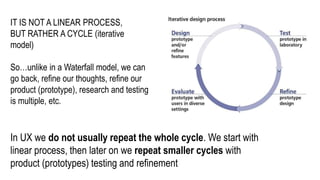
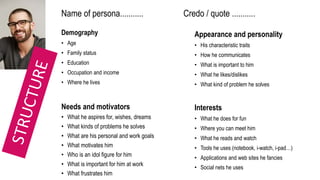
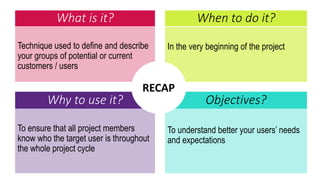
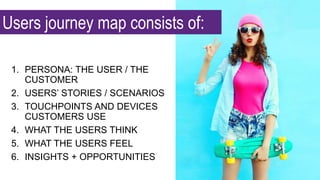
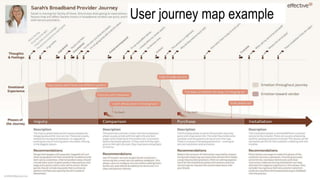
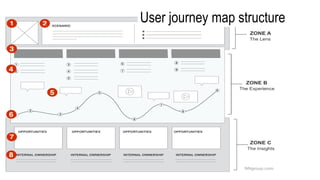
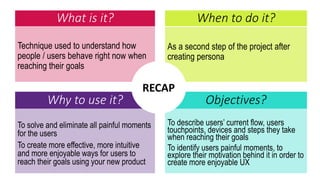
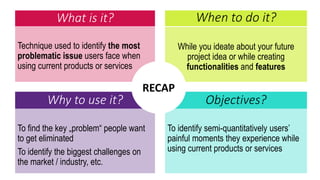
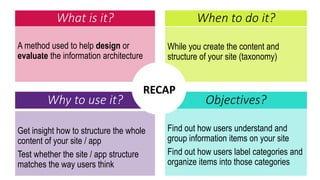
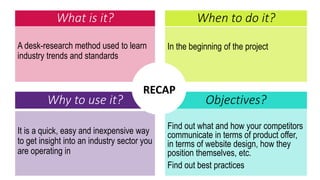
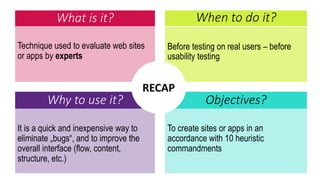
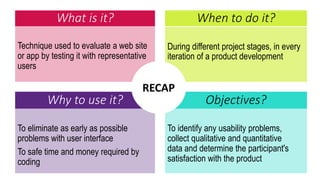
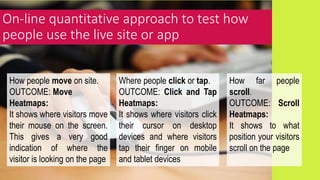
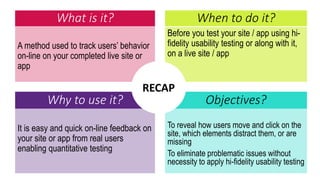
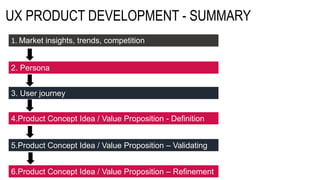
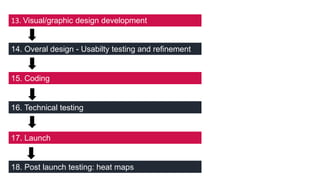
This document provides an overview of user experience (UX) basics, components, goals, and design. It defines UX as encompassing all aspects of a user's interaction with a company, service, or product. The goal of UX design is to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. Key aspects of UX include usability, utility, aesthetics, and emotions. UX research methods are discussed for different stages of product development, including creating personas, user journey mapping, card sorting, heuristic evaluation, and usability testing of prototypes. Usability testing measures how easy products are to use by observing users perform tasks.