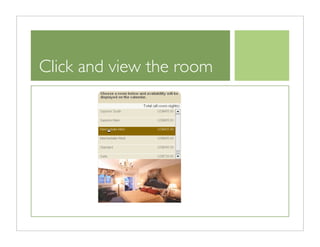
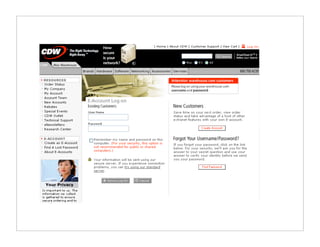
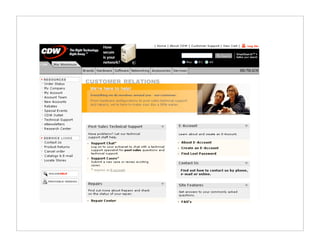
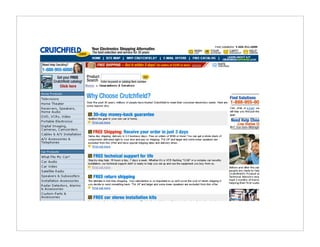
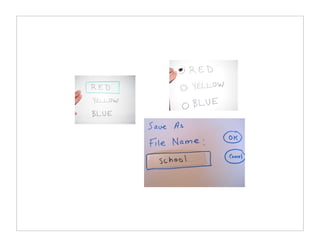
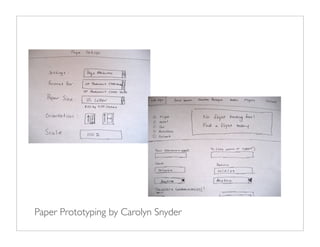
The document outlines quick and effective usability testing techniques tailored for startups, emphasizing the importance of testing with users early in the development process. It includes various methods, such as paper prototyping and five-second tests, to identify design problems and user needs efficiently. Overall, the guidance encourages startups to integrate usability tests to improve product design and better meet customer goals.