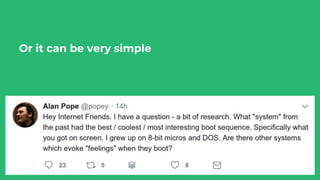
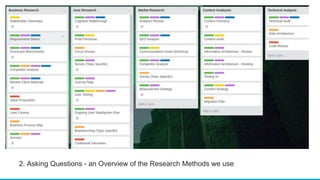
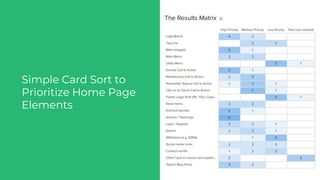
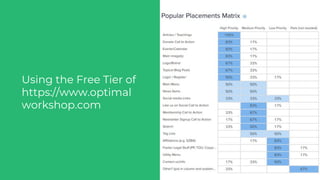
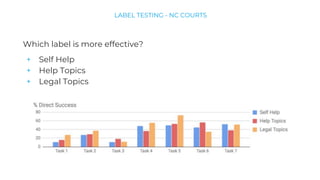
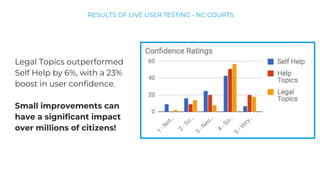
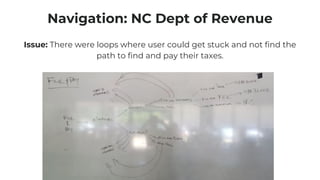
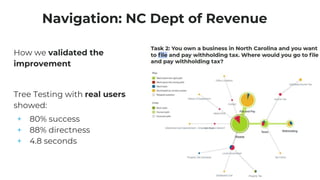
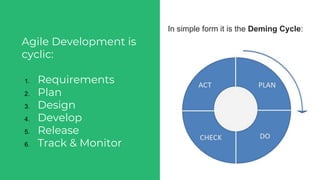
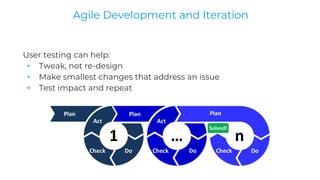
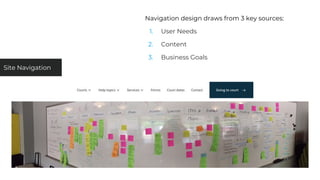
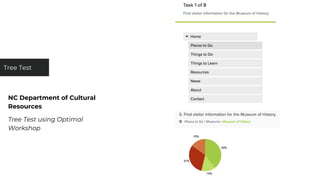
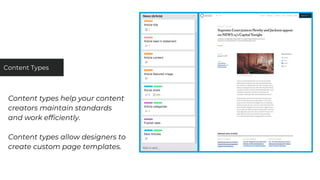
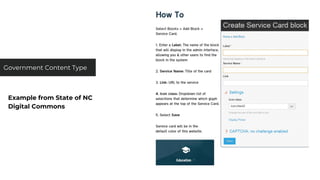
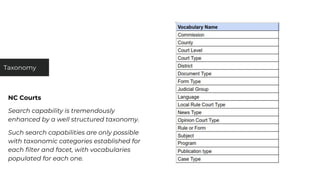
This document discusses various user research methods that can be used to improve open source software and ensure diversity. It begins by explaining the importance of intentionally including a diverse user base to drive innovation. It then provides an overview of common user research methods such as interviews, usability testing, card sorting, and analytics reviews. Specific examples are given around label testing and task-based navigation that resulted in improved user experiences and outcomes. The overall message is that proactively involving and understanding users is critical for the success of any software, including open source projects.