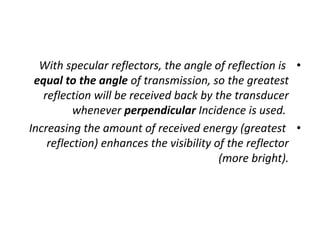
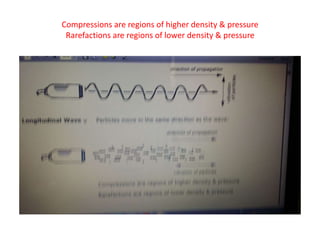
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It works by passing an electric current through a transducer, causing crystals inside to vibrate and produce ultrasound waves. These waves reflect off tissues and organs and return echoes that are converted into images. The frequency of the ultrasound waves determines properties like axial resolution and penetration depth. Ultrasound is widely used for medical imaging due to being noninvasive, painless, and less expensive than other imaging methods.