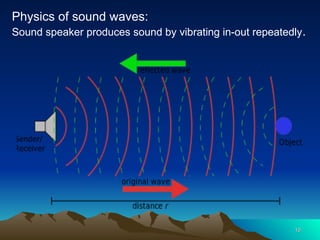
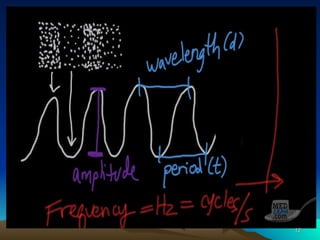
Ultrasonography, or ultrasound, utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of internal organs, primarily by employing a transducer that emits and receives sound echoes. It has various applications in pregnancy, diagnostics, and therapeutic procedures but has limitations in imaging certain body parts. The physics of sound waves, including frequency, amplitude, and acoustic impedance, significantly influence the quality and characteristics of the ultrasound images produced.