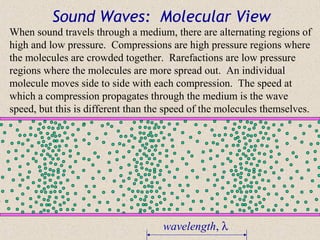
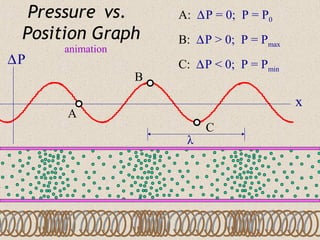
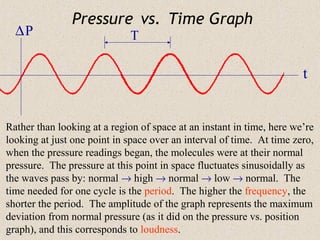
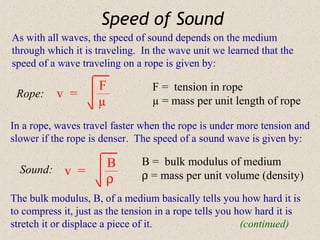
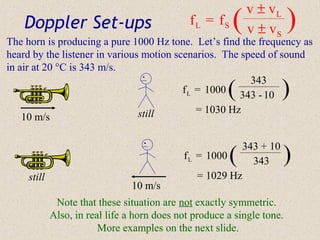
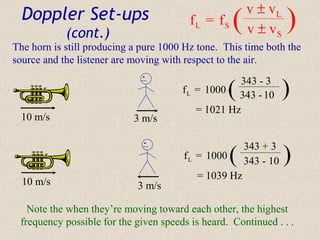
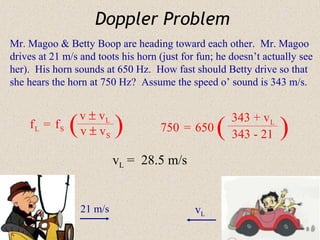
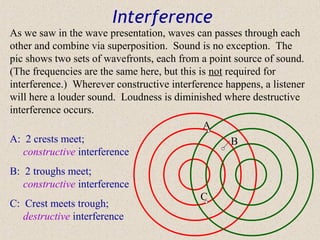
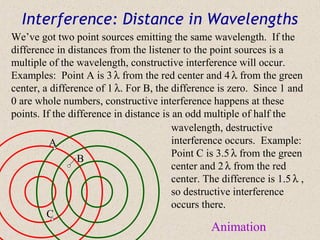
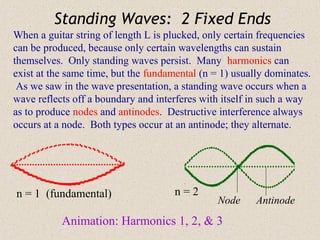
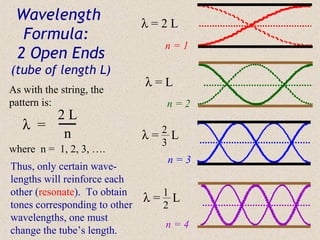
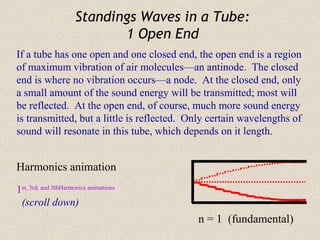
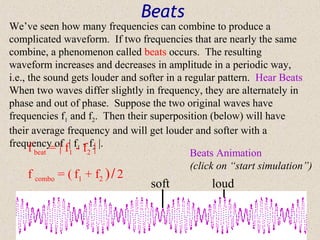
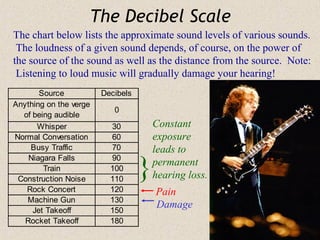
Sound waves are longitudinal waves that propagate through a medium by causing oscillations in pressure. The speed of sound depends on properties of the medium like density and bulk modulus. Frequency determines pitch, with the human hearing range from 20-20,000 Hz. The Doppler effect causes changes in observed frequency due to relative motion between source and receiver. Sonar uses echoes to locate objects by sound, while sonic booms occur when the source moves at or faster than the speed of sound.