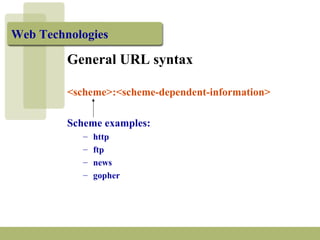
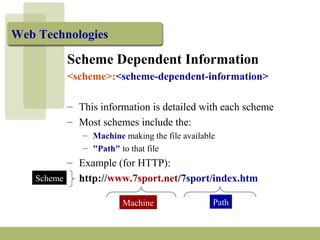
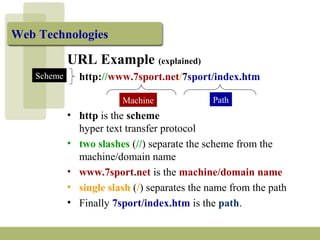
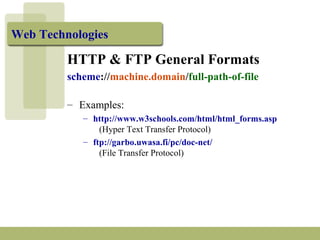
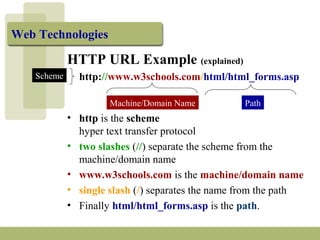
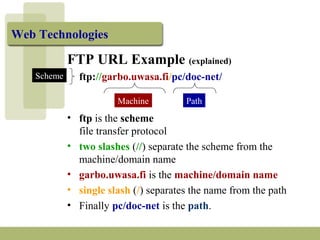
The document discusses URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) and their components. A URL specifies the location of an electronic resource and has the format of <scheme>:<scheme-dependent information>. It explains the different parts of a URL including the scheme (e.g. http, ftp), host/domain name, path, port number (usually omitted), and search parameters. Examples of URLs for both HTTP and FTP are given and their components are described.