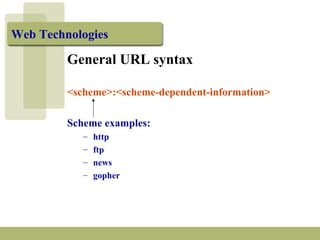
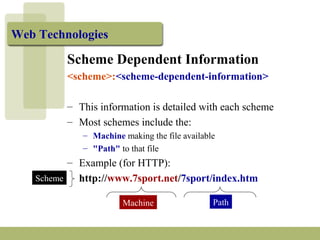
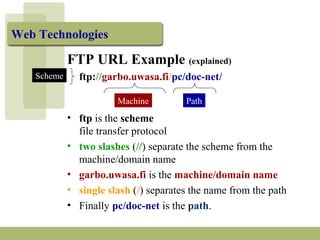
Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) are standardized addresses used to locate resources on the Internet. A URL contains the protocol or scheme being used (such as http or ftp), the domain name or IP address of the server, and the path to the specific file or resource. Well-formed URLs follow a general syntax of <scheme>:<scheme-dependent information>. They allow both humans and software programs to directly access electronic resources. Key components of a URL include the scheme, machine or domain name, and path to the targeted file or resource.